Replication of hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA in mouse embryonic fibroblasts: protein kinase R (PKR)-dependent and PKR-independent mechanisms for controlling HCV RNA replication and mediating interferon activities
- PMID: 16840317
- PMCID: PMC1563689
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00586-06
Replication of hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA in mouse embryonic fibroblasts: protein kinase R (PKR)-dependent and PKR-independent mechanisms for controlling HCV RNA replication and mediating interferon activities
Abstract
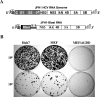
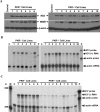
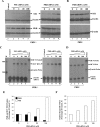
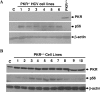
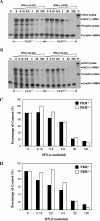
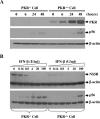
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection causes chronic hepatitis and is currently treated with alpha interferon (IFN-alpha)-based therapies. The underlying mechanisms of chronic HCV infection and IFN-based therapies, however, have not been defined. Protein kinase R (PKR) was implicated in the control of HCV replication and mediation of IFN-induced antiviral response. In this report, we demonstrate that a subgenomic RNA replicon of genotype 2a HCV replicated efficiently in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), as determined by cell colony formation efficiency and the detection of HCV proteins and both positive- and negative-strand RNAs. Additionally, the subgenomic HCV RNA was found to replicate more efficiently in the PKR knockout (PKR(-/-)) MEF than in the wild-type (PKR(+/+)) MEF. The knockdown expression of PKR by specific small interfering RNAs significantly enhanced the level of HCV RNA replication, suggesting that PKR is involved in the control of HCV RNA replication. The level of ISG56 (p56) was induced by HCV RNA replication, indicating the activation of PKR-independent antiviral pathways. Furthermore, IFN-alpha/beta inhibited HCV RNA replication in PKR(-/-) MEFs as efficiently as in PKR(+/+) MEFs. These findings demonstrate that PKR-independent antiviral pathways play important roles in controlling HCV replication and mediating IFN-induced antiviral effect. Our findings also provide a foundation for the development of transgenic mouse models of HCV replication and set a stage to further define the roles of cellular genes in the establishment of chronic HCV infection and the mediation of intracellular innate antiviral response by using MEFs derived from diverse gene knockout animals.
Figures
References
-
- Blight, K. J., A. A. Kolykhalov, and C. M. Rice. 2000. Efficient initiation of HCV RNA replication in cell culture. Science 290:1972-1975. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

