Role for Wee1 in inhibition of G2-to-M transition through the cooperation of distinct human papillomavirus type 1 E4 proteins
- PMID: 16840322
- PMCID: PMC1563741
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00196-06
Role for Wee1 in inhibition of G2-to-M transition through the cooperation of distinct human papillomavirus type 1 E4 proteins
Abstract
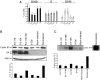
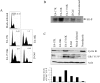
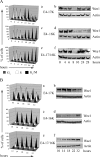
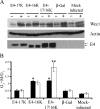
The infectious cycle of human papillomavirus type 1 (HPV1) is accompanied by abundant expression of the full-length E1;E4 protein (17-kDa) and smaller E4 polypeptides (16-, 11-, and 10-kDa) that arise by sequential loss of N-terminal E1;E4 sequences. HPV1 E4 inhibits G(2)-to-M transition of the cell cycle. Here, we show that HPV1 E4 proteins mediate inhibition of cell division by more than one mechanism. Cells arrested by coexpression of E1;E4 (E4-17K) and a truncated protein equivalent to the 16-kDa species (E4-16K) contain inactive cyclin B1-cdk1 complexes. Inactivation of cdk1 is through inhibitory Tyr(15) phosphorylation, with cells containing elevated levels of Wee1, the kinase responsible for inhibitory cdk1 phosphorylation. Consistent with these findings, overexpression of Wee1 enhanced the extent to which E4-17K/16K-expressing cells arrest in G(2), indicating that maintenance of Wee1 activity is necessary for inhibition of cell division induced by coexpression of the two E4 proteins. Moreover, we have determined that depletion of Wee1 by small interfering RNA (siRNA) alleviates the G(2) block imposed by E4-17K/16K. In contrast however, maintenance of Wee1 activity is not necessary for G(2)-to-M inhibition mediated by E4-16K alone, as overexpression or depletion of Wee1 does not influence the G(2) arrest function of E4-16K. Cells arrested by E4-16K expression contain low levels of active cyclin B1-cdk1 complexes. We hypothesize that differential expression of HPV1 E4 proteins during the viral life cycle determines the host cell cycle status. Different mechanisms of inhibition of G(2)-to-M transition reinforce the supposition that distinct E4 functions are important for HPV replication.
Figures




References
-
- Ashmole, I., P. H. Gallimore, and S. Roberts. 1998. Identification of conserved hydrophobic C-terminal residues of the human papillomavirus type 1 E1E4 protein necessary for E4 oligomerisation in vivo. Virology 240:221-231. - PubMed
-
- Boudreau, R. T., and D. W. Hoskin. 2005. The use of okadaic acid to elucidate the intracellular role(s) of protein phosphatase 2A: lessons from the mast cell model system. Int. Immunopharmacol. 5:1507-1518. - PubMed
-
- Breitburd, F., O. Croissant, and G. Orth. 1987. Expression of human papillomavirus type-1 E4 gene products in warts, p. 115-122. In B. M. Steinberg, J. Brandsma, and L. B. Taichman (ed.), Papillomaviruses: cancer cells, vol. 5. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
-
- Brown, D. R., C. R. Brown, and E. E. Lehr. 2004. Intracellular expression patterns of the human papillomavirus type 59 E1/E4 protein in COS cells, keratinocytes, and genital epithelium. Intervirology 47:321-327. - PubMed
-
- Davy, C. E., D. J. Jackson, K. Raj, W. L. Peh, S. A. Southern, P. Das, R. Sorathia, P. Laskey, K. Middleton, T. Nakahara, Q. Wang, P. J. Masterson, P. F. Lambert, S. Cuthill, J. B. Millar, and J. Doorbar. 2005. Human papillomavirus type 16 E1^E4-induced G2 arrest is associated with cytoplasmic retention of active Cdk1/cyclin B1 complexes. J. Virol. 79:3998-4011. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

