Cytomegalovirus encodes a positive regulator of antigen presentation
- PMID: 16840340
- PMCID: PMC1563742
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00723-06
Cytomegalovirus encodes a positive regulator of antigen presentation
Abstract
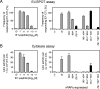
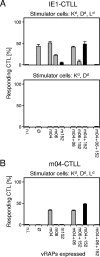
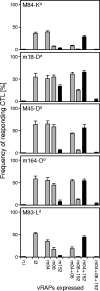
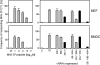
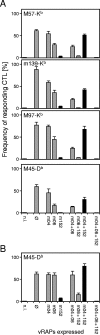
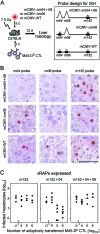
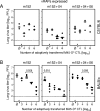
Murine cytomegalovirus encodes three regulators of antigen presentation to antiviral CD8 T cells. According to current paradigms, all three regulators are committed to the inhibition of the presentation of antigenic peptides. Whereas m152/gp40 catalyzes the retention of peptide-loaded major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules in a cis-Golgi compartment, m06/gp48 binds stably to class I molecules and directs them into the cellular cargo-sorting pathway of lysosomal degradation. Regulator m04/gp34 also binds stably to class I molecules, but unlike m152 and m06, it does not downmodulate MHC class I cell surface expression. It has entered the literature as a direct inhibitor of T-cell recognition of the MHC-peptide complex at the cell surface. In this work, we have studied the presentation of antigenic viral peptides in cells infected with a comprehensive set of mutant viruses expressing the three regulators separately as well as in all possible combinations. The results redefine m04 as a positive regulator dedicated to the facilitation of antigen presentation. When expressed alone, it did not inhibit T-cell recognition, and when expressed in the presence of m152, it restored antigen presentation by antagonizing the inhibitory function of m152. Its intrinsic positive function, however, was antagonized and even slightly overcompensated for by the negative regulator m06. In an adoptive cell transfer model, the opposing forces of the three regulators were found to govern immune surveillance in the infected host. While negative regulators, also known as immunoevasins, are common, the existence of a positive regulator is without precedent and indicates an intriguing genetic potential of this virus to influence antigen presentation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The putative natural killer decoy early gene m04 (gp34) of murine cytomegalovirus encodes an antigenic peptide recognized by protective antiviral CD8 T cells.J Virol. 2000 Feb;74(4):1871-84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.4.1871-1884.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10644360 Free PMC article.
-
The immune evasion paradox: immunoevasins of murine cytomegalovirus enhance priming of CD8 T cells by preventing negative feedback regulation.J Virol. 2008 Dec;82(23):11637-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01510-08. Epub 2008 Sep 24. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18815306 Free PMC article.
-
Positive Role of the MHC Class-I Antigen Presentation Regulator m04/gp34 of Murine Cytomegalovirus in Antiviral Protection by CD8 T Cells.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Aug 26;10:454. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00454. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32984075 Free PMC article.
-
Stalemating a clever opportunist: lessons from murine cytomegalovirus.Hum Immunol. 2004 May;65(5):446-55. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2004.02.024. Hum Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15172444 Review.
-
Cytomegaloviral control of MHC class I function in the mouse.Immunol Rev. 1999 Apr;168:167-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01291.x. Immunol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10399073 Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired direct priming of CD8 T cells by donor-derived cytomegalovirus following kidney transplantation.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013 Oct;24(10):1698-708. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013040340. Epub 2013 Jul 11. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23847277 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant viruses as tools to study human cytomegalovirus immune modulation.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2008 Jun;197(2):215-22. doi: 10.1007/s00430-008-0083-4. Epub 2008 Feb 27. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18301917 Review.
-
Transactivation of cellular genes involved in nucleotide metabolism by the regulatory IE1 protein of murine cytomegalovirus is not critical for viral replicative fitness in quiescent cells and host tissues.J Virol. 2008 Oct;82(20):9900-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00928-08. Epub 2008 Aug 6. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18684825 Free PMC article.
-
The structure of mouse cytomegalovirus m04 protein obtained from sparse NMR data reveals a conserved fold of the m02-m06 viral immune modulator family.Structure. 2014 Sep 2;22(9):1263-1273. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2014.05.018. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Structure. 2014. PMID: 25126960 Free PMC article.
-
Cytomegalovirus immune evasion sets the functional avidity threshold for protection by CD8 T cells.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2023 Apr;212(2):153-163. doi: 10.1007/s00430-022-00733-w. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 35364731 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Del Val, M., H. Hengel, H. Haecker, U. Hartlaub, T. Ruppert, P. Lucin, and U. H. Koszinowski. 1992. Cytomegalovirus prevents antigen presentation by blocking the transport of peptide-loaded major histocompatibility complex class I molecules into the medial-Golgi compartment. J. Exp. Med. 176:729-738. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gold, M. C., M. W. Munks, M. Wagner, U. H. Koszinowski, A. B. Hill, and S. P. Fling. 2002. The murine cytomegalovirus immunomodulatory gene m152 prevents recognition of infected cells by M45-specific CTL, but does not alter the immunodominance of the M45-specific CD8 T cell response in vivo. J. Immunol. 169:359-365. - PubMed
-
- Gold, M. C., M. W. Munks, M. Wagner, C. W. McMahon, A. Kelly, D. G. Kavanagh, M. K. Slifka, U. H. Koszinowski, D. H. Raulet, and A. B. Hill. 2004. Murine cytomegalovirus interference with antigen presentation has little effect on the size or the effector memory phenotype of the CD8 T cell response. J. Immunol. 172:6944-6953. - PubMed
-
- Harlow, E., and D. Lane. 1988. Antibodies: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

