Alpha interferon potently enhances the anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 activity of APOBEC3G in resting primary CD4 T cells
- PMID: 16840343
- PMCID: PMC1563726
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00206-06
Alpha interferon potently enhances the anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 activity of APOBEC3G in resting primary CD4 T cells
Abstract
The interferon (IFN) system, including various IFNs and IFN-inducible gene products, is well known for its potent innate immunity against wide-range viruses. Recently, a family of cytidine deaminases, functioning as another innate immunity against retroviral infection, has been identified. However, its regulation remains largely unknown. In this report, we demonstrate that through a regular IFN-alpha/beta signal transduction pathway, IFN-alpha can significantly enhance the expression of apolipoprotein B mRNA-editing enzyme-catalytic polypeptide-like 3G (APOBEC3G) in human primary resting but not activated CD4 T cells and the amounts of APOBEC3G associated with a low molecular mass. Interestingly, short-time treatments of newly infected resting CD4 T cells with IFN-alpha will significantly inactivate human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) at its early stage. This inhibition can be counteracted by APOBEC3G-specific short interfering RNA, indicating that IFN-alpha-induced APOBEC3G plays a key role in mediating this anti-HIV-1 process. Our data suggest that APOBEC3G is also a member of the IFN system, at least in resting CD4 T cells. Given that the IFN-alpha/APOBEC3G pathway has potent anti-HIV-1 capability in resting CD4 T cells, augmentation of this innate immunity barrier could prevent residual HIV-1 replication in its native reservoir in the post-highly active antiretroviral therapy era.
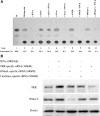
Figures
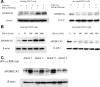

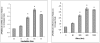




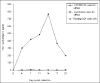
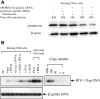

Similar articles
-
Cellular APOBEC3G restricts HIV-1 infection in resting CD4+ T cells.Nature. 2005 May 5;435(7038):108-14. doi: 10.1038/nature03493. Epub 2005 Apr 13. Nature. 2005. Retraction in: Nature. 2010 Jul 8;466(7303):276. doi: 10.1038/nature09254. PMID: 15829920 Retracted.
-
Induction of APOBEC3 family proteins, a defensive maneuver underlying interferon-induced anti-HIV-1 activity.J Exp Med. 2006 Jan 23;203(1):41-6. doi: 10.1084/jem.20051512. Epub 2006 Jan 17. J Exp Med. 2006. PMID: 16418394 Free PMC article.
-
IFN-α induces APOBEC3G, F, and A in immature dendritic cells and limits HIV-1 spread to CD4+ T cells.J Immunol. 2013 Apr 1;190(7):3346-53. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201184. Epub 2013 Feb 20. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23427247
-
APOBEC deaminases as cellular antiviral factors: a novel natural host defense mechanism.Med Sci Monit. 2006 May;12(5):RA92-8. Med Sci Monit. 2006. PMID: 16641889 Review.
-
Protecting APOBEC3G: a potential new target for HIV drug discovery.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2005 Feb;6(2):141-7. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2005. PMID: 15751736 Review.
Cited by
-
Viral Coinfections.Viruses. 2022 Nov 26;14(12):2645. doi: 10.3390/v14122645. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36560647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between Intrinsic and Innate Immunity during HIV Infection.Cells. 2019 Aug 17;8(8):922. doi: 10.3390/cells8080922. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31426525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WFDC1/ps20 is a novel innate immunomodulatory signature protein of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-permissive CD4+ CD45RO+ memory T cells that promotes infection by upregulating CD54 integrin expression and is elevated in HIV type 1 infection.J Virol. 2008 Jan;82(1):471-86. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00939-07. Epub 2007 Oct 17. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 17942534 Free PMC article.
-
T cells contain an RNase-insensitive inhibitor of APOBEC3G deaminase activity.PLoS Pathog. 2007 Sep 21;3(9):1320-34. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030135. PLoS Pathog. 2007. PMID: 17892323 Free PMC article.
-
Implication of TRIM alpha and TRIMCyp in interferon-induced anti-retroviral restriction activities.Retrovirology. 2008 Jul 9;5:59. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-5-59. Retrovirology. 2008. PMID: 18613956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berglund, O., K. Engman, A. Ehrnst, J. Andersson, K. Lidman, B. Akerlund, A. Sonnerborg, and O. Strannegard. 1991. Combined treatment of symptomatic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection with native interferon-alpha and zidovudine. J. Infect. Dis. 163:710-715. - PubMed
-
- Bishop, K. N., R. K. Holmes, A. M. Sheehy, N. O. Davidson, S. J. Cho, and M. H. Malim. 2004. Cytidine deamination of retroviral DNA by diverse APOBEC proteins. Curr. Biol. 14:1392-1396. - PubMed
-
- Chiu, Y. L., V. B. Soros, J. F. Kreisberg, K. Stopak, W. Yonemoto, and W. C. Greene. 2005. Cellular APOBEC3G restricts HIV-1 infection in resting CD4+ T cells. Nature 435:108-114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

