Facial thermography is a sensitive tool to determine antihistaminic activity: comparison of levocetirizine and fexofenadine
- PMID: 16842390
- PMCID: PMC1885088
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2006.02647.x
Facial thermography is a sensitive tool to determine antihistaminic activity: comparison of levocetirizine and fexofenadine
Abstract
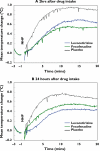
Aims: To assess the antihistaminic activity of levocetirizine and fexofenadine 2 h and 24 h after drug administration using facial thermography and to compare the results with those using well-established parameters of antihistaminic activity in the nose and skin.
Methods: This was a randomized, double-blind, three-treatment, three-period, single-dose, cross-over study in healthy males taking levocetirizine 5 mg, fexofenadine 120 mg or placebo. The primary endpoint was nasal skin temperature after nasal histamine challenge recorded for 20 min at 2 and 24 h after drug intake. The secondary endpoints were nasal symptoms and a histamine skin prick test.
Results: Thirty subjects were randomized. At 2 h after drug intake the inhibition of the nasal temperature increase from baseline was not significantly different between levocetirizine and fexofenadine. At 24 h it was significantly more pronounced after levocetirizine than fexofenadine (difference: least-squares mean: -0.13 degrees C; P < or = 0.024, 95% CI -0.24, -0.02). Both drugs significantly reduced (P < or = 0.001) the mean temperature increase from baseline compared with placebo at 2 and 24 h (least-squares mean increase and (95% CI): levocetirizine, -0.28 degrees C (-0.42, -0.14) and -0.32 degrees C (-0.43, -0.21); fexofenadine -0.35 degrees C (-0.49, -0.21) and -0.19 degrees C (-0.30, -0.08), respectively). Results of nasal symptom score and wheal and flare were consistent with the thermography results.
Conclusions: Facial thermography is an objective, non-invasive and sensitive method to study antihistaminic activity at the nose level. Levocetirizine and fexofenadine demonstrate the same activity at 2 h after drug intake, but levocetirizine has a more sustained activity at 24 h.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Levocetirizine has a longer duration of action on improving total nasal symptoms score than fexofenadine after single administration.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005 Jul;60(1):24-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02377.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15963090 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[The effect of 5-days of cetirizine, desloratadine, fexofenadine 120 and 180 mg, levocetirizine, loratadine treatment on the histamine-induced skin reaction and skin blood flow--a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2006 Nov;21(125):449-53. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2006. PMID: 17345838 Clinical Trial. Polish.
-
Twenty-four hours of activity of cetirizine and fexofenadine in the skin.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001 Apr;86(4):387-92. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)62483-0. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11345280 Clinical Trial.
-
A review of the efficacy of desloratadine, fexofenadine, and levocetirizine in the treatment of nasal congestion in patients with allergic rhinitis.Clin Ther. 2009 May;31(5):921-44. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.05.017. Clin Ther. 2009. PMID: 19539095 Review.
-
Comparison of pharmacokinetics and metabolism of desloratadine, fexofenadine, levocetirizine and mizolastine in humans.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2004 Aug;18(4):399-411. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2004.00254.x. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15312146 Review.
Cited by
-
Once daily levocetirizine for the treatment of allergic rhinitis and chronic idiopathic urticaria.J Asthma Allergy. 2008 Dec 16;2:17-23. doi: 10.2147/jaa.s3022. J Asthma Allergy. 2008. PMID: 21437140 Free PMC article.
-
Halo formations around senile hemangiomas in diffuse plane normolipemic xanthomatosis associated with monoclonal gammopathy.JAAD Case Rep. 2018 Nov 10;4(10):1034-1036. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2018.08.012. eCollection 2018 Nov. JAAD Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 30456279 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Update on prescription and over-the-counter histamine inverse agonists in rhinitis therapy.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2009 Mar;9(2):140-8. doi: 10.1007/s11882-009-0021-6. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2009. PMID: 19210904
-
Investigation of the antiallergic activity of olopatadine on rhinitis induced by intranasal instillation of antigen in sensitized rats using thermography.Asia Pac Allergy. 2011 Oct;1(3):138-44. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2011.1.3.138. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Asia Pac Allergy. 2011. PMID: 22053310 Free PMC article.
-
Antihistamine effects and safety of fexofenadine: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019 Nov 29;20(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s40360-019-0363-1. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31783781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akdis CA, Blaser K. Histamine in the immune regulation of allergic inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;112:15–22. - PubMed
-
- MacGlashan D., Jr Histamine: a mediator of inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;112:S53–S59. - PubMed
-
- Estelle F, Simons R. Advances in H1-antihistamines. N Eng J Med. 2004;351:2203–17. - PubMed
-
- Denham KJ, Boutsiouki P, Clough GF, Church MK. Comparison of the effects of desloratadine and levocetirizine on histamine-induced wheal, flare and itch in human skin. Inflamm Res. 2003;52:424–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

