Domain-swapped structure of the potent antiviral protein griffithsin and its mode of carbohydrate binding
- PMID: 16843894
- PMCID: PMC7126681
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2006.05.017
Domain-swapped structure of the potent antiviral protein griffithsin and its mode of carbohydrate binding
Abstract
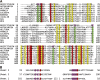
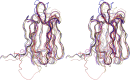
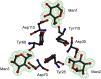
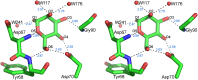
The crystal structure of griffithsin, an antiviral lectin from the red alga Griffithsia sp., was solved and refined at 1.3 A resolution for the free protein and 0.94 A for a complex with mannose. Griffithsin molecules form a domain-swapped dimer, in which two beta strands of one molecule complete a beta prism consisting of three four-stranded sheets, with an approximate 3-fold axis, of another molecule. The structure of each monomer bears close resemblance to jacalin-related lectins, but its dimeric structure is unique. The structures of complexes of griffithsin with mannose and N-acetylglucosamine defined the locations of three almost identical carbohydrate binding sites on each monomer. We have also shown that griffithsin is a potent inhibitor of the coronavirus responsible for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Antiviral potency of griffithsin is likely due to the presence of multiple, similar sugar binding sites that provide redundant attachment points for complex carbohydrate molecules present on viral envelopes.
Figures

Comment in
-
Common scaffolds, diverse recognition profiles.Structure. 2006 Jul;14(7):1093-4. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2006.06.001. Structure. 2006. PMID: 16843888 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams E.W., Ratner D.M., Bokesch H.R., McMahon J.B., O'Keefe B.R., Seeberger P.H. Oligosaccharide and glycoprotein microarrays as tools in HIV glycobiology; glycan-dependent gp120/protein interactions. Chem. Biol. 2004;11:875–881. - PubMed
-
- Aucouturier P., Mihaesco E., Mihaesco C., Preud'homme J.L. Characterization of jacalin, the human IgA and IgD binding lectin from jackfruit. Mol. Immunol. 1987;24:503–511. - PubMed
-
- Bokesch H.R., O'Keefe B.R., McKee T.C., Pannell L.K., Patterson G.M., Gardella R.S., Sowder R.C., Turpin J., Watson K., Buckheit R.W., Jr., Boyd M.R. A potent novel anti-HIV protein from the cultured cyanobacterium Scytonema varium. Biochemistry. 2003;42:2578–2584. - PubMed
-
- Bolmstedt A.J., O'Keefe B.R., Shenoy S.R., McMahon J.B., Boyd M.R. Cyanovirin-N defines a new class of antiviral agent targeting N-linked, high-mannose glycans in an oligosaccharide-specific manner. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001;59:949–954. - PubMed
-
- Botos I., Wlodawer A. Proteins that bind high-mannose sugars of the HIV envelope. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2005;88:233–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

