Optimization and functional effects of stable short hairpin RNA expression in primary human lymphocytes via lentiviral vectors
- PMID: 16844419
- PMCID: PMC2562632
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2006.05.015
Optimization and functional effects of stable short hairpin RNA expression in primary human lymphocytes via lentiviral vectors
Abstract
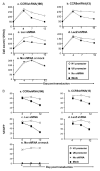
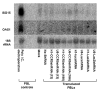
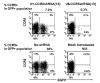
Specific, potent, and sustained short hairpin RNA (shRNA)-mediated gene silencing is crucial for the successful application of RNA interference technology to therapeutic interventions. We examined the effects of shRNA expression in primary human lymphocytes (PBLs) using lentiviral vectors bearing different RNA polymerase III promoters. We found that the U6 promoter is more efficient than the H1 promoter for shRNA expression and for reducing expression of CCR5 in PBLs. However, shRNA expression from the U6 promoter resulted in a gradual decline of the transduced cell populations. With one CCR5 shRNA this decline could be attributed to elevated apoptosis but another CCR5 shRNA that caused cytotoxicity did not show evidence of apoptosis, suggesting sequence-specific mechanisms for cytotoxicity. In contrast to the U6 promoter, PBLs transduced by vectors expressing shRNAs from the H1 promoter could be maintained without major cytotoxic effects. Since a lower level of shRNA expression appears to be advantageous to maintaining the shRNA-transduced population, lentiviral vectors bearing the H1 promoter are more suitable for stable transduction and expression of shRNA in primary human T lymphocytes. Our results suggest that functional shRNA screens should include tests for both potency and adverse metabolic effects upon primary cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Determinants of interferon-stimulated gene induction by RNAi vectors.Differentiation. 2004 Mar;72(2-3):103-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.2004.07202001.x. Differentiation. 2004. PMID: 15066190
-
Of mice and men: human RNA polymerase III promoter U6 is more efficient than its murine homologue for shRNA expression from a lentiviral vector in both human and murine progenitor cells.Exp Hematol. 2010 Sep;38(9):792-7. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2010.05.005. Epub 2010 May 26. Exp Hematol. 2010. PMID: 20685233
-
Lentiviral vector design for multiple shRNA expression and durable HIV-1 inhibition.Mol Ther. 2008 Mar;16(3):557-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.mt.6300382. Epub 2008 Jan 15. Mol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18180777 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term cytotoxic effects and long-term instability of RNAi delivered using lentiviral vectors.BMC Mol Biol. 2004 Aug 3;5:9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-5-9. BMC Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15291968 Free PMC article.
-
DNA vector-based RNA interference to study gene function in cancer.J Vis Exp. 2012 Jun 4;(64):e4129. doi: 10.3791/4129. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 22710444 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Efficient inhibition of HIV-1 replication by an artificial polycistronic miRNA construct.Virol J. 2012 Jun 18;9:118. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-118. Virol J. 2012. PMID: 22709537 Free PMC article.
-
Stem cell gene therapy for HIV: strategies to inhibit viral entry and replication.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2015 Mar;12(1):79-87. doi: 10.1007/s11904-014-0242-8. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2015. PMID: 25578054 Review.
-
CCR5 as a natural and modulated target for inhibition of HIV.Viruses. 2013 Dec 30;6(1):54-68. doi: 10.3390/v6010054. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 24381033 Free PMC article.
-
Development of hematopoietic stem cell based gene therapy for HIV-1 infection: considerations for proof of concept studies and translation to standard medical practice.Viruses. 2013 Nov 22;5(11):2898-919. doi: 10.3390/v5112898. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 24284880 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lentiviral vector-mediated RNA silencing in the central nervous system.Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2014 Feb;25(1):14-32. doi: 10.1089/hgtb.2013.016. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2014. PMID: 24090197 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hannon GJ. RNA interference. Nature. 2002;418:244–251. - PubMed
-
- Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W, Yalcin A, Weber K, Tuschl T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 2001;411:494–498. - PubMed
-
- Lee NS, et al. Expression of small interfering RNAs targeted against HIV-1 rev transcripts in human cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20:500–505. - PubMed
-
- Miyagishi M, Taira K. U6 promoter driven siRNAs with four uridine 3′ overhangs efficiently suppress targeted gene expression in mammalian cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20:497–500. - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science. 2002;296:550–553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

