Network modulation in the treatment of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 16844713
- PMCID: PMC4459513
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awl162
Network modulation in the treatment of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
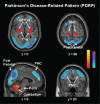
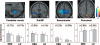
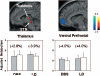
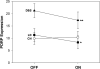
It has been proposed that deep brain stimulation (DBS) of the subthalamic nucleus (STN DBS) and dopaminergic therapy ameliorate the symptoms of Parkinson's disease through similar functional mechanisms. We examined this notion using PET to compare the metabolic effects of these treatment approaches. Nine Parkinson's disease patients (age 61.7 +/- 11.1 years) were scanned ON and OFF STN stimulation and nine others (age 60.0 +/- 9.3 years) were scanned ON and OFF an individual titrated intravenous levodopa infusion. The two treatment groups were matched for baseline disease severity as well as clinical response to therapy. Similarities and differences in the effects of treatment on regional metabolism were assessed using statistical parametric mapping (SPM). In addition, we used network analysis to assess the effect of therapy on the expression of an abnormal Parkinson's disease-related spatial covariance pattern (PDRP). We found that both STN DBS and levodopa therapy were associated with significant (P < 0.001) metabolic reductions in the putamen/globus pallidus, sensorimotor cortex and cerebellar vermis, as well as increases in the precuneus (BA 7). The metabolic effects of the two interventions differed in the STN and medial prefrontal cortex, with relative increases with stimulation in the former structure and decreases in the latter. Network quantification disclosed reductions in PDRP activity with both interventions, which correlated with clinical improvement (P < 0.05). The degree of network modulation by therapy did not differ significantly for the two treatment approaches (P > 0.6). These findings support the results of previous imaging studies indicating that effective symptomatic therapies for Parkinson's disease involve a common mechanism. The modulation of pathological brain networks is a critical feature of the treatment response in parkinsonism.
Figures

References
-
- Asanuma K, Ma Y, Huang C, Carbon M, Edwards C, Raymond D, et al. The metabolic pathology of dopa-responsive dystonia. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:596–600. - PubMed
-
- Beck A. Beck depression inventory: manual. Psychological Corporation; San Antonio: 1987.
-
- Benabid AL. Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003;13:696–706. - PubMed
-
- Benazzouz A, Hallett M. Mechanism of action of deep brain stimulation. Neurology. 2000;55:S13–6. - PubMed
-
- Benton A, Hamsher K, Sivan A. Multilingual aphasia examination. 3rd edn. AJA Associates; Iowa City: 1994.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

