A molecular dynamics study and free energy analysis of complexes between the Mlc1p protein and two IQ motif peptides
- PMID: 16844751
- PMCID: PMC1562369
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.106.085399
A molecular dynamics study and free energy analysis of complexes between the Mlc1p protein and two IQ motif peptides
Abstract
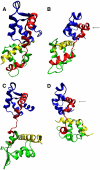
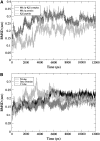
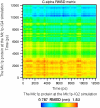
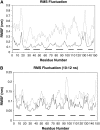
The Mlc1p protein from the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a Calmodulin-like protein, which interacts with IQ-motif peptides located at the yeast's myosin neck. In this study, we report a molecular dynamics study of the Mlc1p-IQ2 protein-peptide complex, starting with its crystal structure, and investigate its dynamics in an aqueous solution. The results are compared with those obtained by a previous study, where we followed the solution structure of the Mlc1p-IQ4 protein-peptide complex by molecular dynamics simulations. After the simulations, we performed an interaction free-energy analysis using the molecular mechanics Poisson-Boltzmann surface area approach. Based on the dynamics of the Mlc1p-IQ protein-peptide complexes, the structure of the light-chain-binding domain of myosin V from the yeast S. cerevisiae is discussed.
Figures

References
-
- Yamniuk, A. P., and H. J. Vogel. 2004. Calmodulin's flexibility allows for promiscuity in its interactions with target proteins and peptides. Mol. Biotechnol. 27:33–57. - PubMed
-
- Chin, D., and A. R. Means. 2000. Calmodulin: a prototypical calcium sensor. Trends Cell Biol. 10:322–328. - PubMed
-
- Vogel, H. J., R. D. Brokx, and H. Ouyang. 2002. Calcium-binding proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 172:3–20. - PubMed
-
- Wilson, M. A., and A. T. Brunger. 2000. The 1.0 Å crystal structure of Ca2+-bound calmodulin: an analysis of disorder and implications for functionally relevant plasticity. J. Mol. Biol. 301:1237–1256. - PubMed
-
- Yun, C. H., J. Bai, D. Y. Sun, D. F. Cui, W. R. Chang, and D. C. Liang. 2004. Structure of potato calmodulin PCM6: the first report of the three-dimensional structure of a plant calmodulin. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60:1214–1219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

