T lineage differentiation from human embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 16844782
- PMCID: PMC1544240
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0604244103
T lineage differentiation from human embryonic stem cells
Abstract
Harnessing the ability of genetically manipulated human embryonic stem cells (hESC) to differentiate into appropriate lineages could revolutionize medical practice. These cells have the theoretical potential to develop into all mature cell types; however, the actual ability to develop into all hematopoietic lineages has not been demonstrated. Using sequential in vitro coculture on murine bone marrow stromal cells, and engraftment into human thymic tissues in immunodeficient mice, we demonstrate that hESC can differentiate through the T lymphoid lineage. Stable transgene expression was maintained at high levels throughout differentiation, suggesting that genetically manipulated hESC hold potential to treat several T cell disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
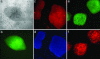



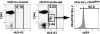

Comment in
-
Embryonic stem cells make human T cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 15;103(33):12213-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605344103. Epub 2006 Aug 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16894150 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Chadwick K., Wang L., Li L., Menendez P., Murdoch B., Rouleau A., Bhatia M. Blood. 2003;102:906–915. - PubMed
-
- Vodyanik M. A., Bork J. A., Thomson J. A., Slukvin I. I. Blood. 2005;105:617–626. - PubMed
-
- Slukvin I. I., Vodyanik M. A., Thomson J. A., Gumenyuk M. E., Choi K. D. J. Immunol. 2006;176:2924–2932. - PubMed
-
- Woll P. S., Martin C. H., Miller J. S., Kaufman D. S. J. Immunol. 2005;175:5095–5103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

