Arabidopsis CULLIN4 Forms an E3 Ubiquitin Ligase with RBX1 and the CDD Complex in Mediating Light Control of Development
- PMID: 16844902
- PMCID: PMC1533989
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.106.043224
Arabidopsis CULLIN4 Forms an E3 Ubiquitin Ligase with RBX1 and the CDD Complex in Mediating Light Control of Development
Abstract
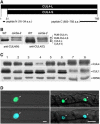
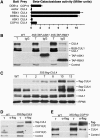
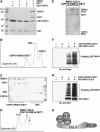
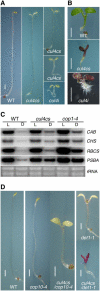
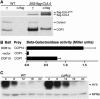
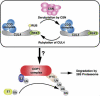
Repression of photomorphogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana requires activity of the COP9 signalosome (CSN), CDD, and COP1 complexes, but how these three complexes work in concert to accomplish this important developmental switch has remained unknown. Here, we demonstrate that Arabidopsis CULLIN4 (CUL4) associates with the CDD complex and a common catalytic subunit to form an active E3 ubiquitin ligase both in vivo and in vitro. The partial loss of function of CUL4 resulted in a constitutive photomorphogenic phenotype with respect to morphogenesis and light-regulated gene expression. Furthermore, CUL4 exhibits a synergistic genetic interaction with COP10 and DET1. Therefore, this CUL4-based E3 ligase is essential for the repression of photomorphogenesis. This CUL4-based E3 ligase appears to associate physically with COP1 E3 ligase and positively regulates the COP1-dependent degradation of photomorphogenesis-promoting transcription factors, whereas the CSN controls the biochemical modification of CUL4 essential for E3 activity. Thus, this study suggests a biochemical activity connection between CSN and CDD complexes in their cooperation with COP1 in orchestrating the repression of photomorphogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ubiquitin ligase switch in plant photomorphogenesis: A hypothesis.J Theor Biol. 2011 Feb 7;270(1):31-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2010.11.021. Epub 2010 Nov 18. J Theor Biol. 2011. PMID: 21093457 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis CULLIN4-damaged DNA binding protein 1 interacts with CONSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1-SUPPRESSOR OF PHYA complexes to regulate photomorphogenesis and flowering time.Plant Cell. 2010 Jan;22(1):108-23. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.065490. Epub 2010 Jan 8. Plant Cell. 2010. PMID: 20061554 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis DDB1-CUL4 ASSOCIATED FACTOR1 forms a nuclear E3 ubiquitin ligase with DDB1 and CUL4 that is involved in multiple plant developmental processes.Plant Cell. 2008 Jun;20(6):1437-55. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.058891. Epub 2008 Jun 13. Plant Cell. 2008. PMID: 18552200 Free PMC article.
-
The photomorphogenic repressors COP1 and DET1: 20 years later.Trends Plant Sci. 2012 Oct;17(10):584-93. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2012.05.004. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Trends Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22705257 Review.
-
Constitutive photomorphogenesis protein 1 (COP1) and COP9 signalosome, evolutionarily conserved photomorphogenic proteins as possible targets of melatonin.J Pineal Res. 2016 Aug;61(1):41-51. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12340. Epub 2016 Jun 13. J Pineal Res. 2016. PMID: 27121162 Review.
Cited by
-
The Arabidopsis DDB1 interacting protein WDR55 is required for vegetative development.Plant Signal Behav. 2013 Sep;8(9):e25347. doi: 10.4161/psb.25347. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Plant Signal Behav. 2013. PMID: 23803743 Free PMC article.
-
DWA1 and DWA2, two Arabidopsis DWD protein components of CUL4-based E3 ligases, act together as negative regulators in ABA signal transduction.Plant Cell. 2010 Jun;22(6):1716-32. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.073783. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Plant Cell. 2010. PMID: 20525848 Free PMC article.
-
Plant biology research comes of age in China.Plant Cell. 2006 Nov;18(11):2855-64. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.045393. Plant Cell. 2006. PMID: 17170389 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The conserved factor DE-ETIOLATED 1 cooperates with CUL4-DDB1DDB2 to maintain genome integrity upon UV stress.EMBO J. 2011 Mar 16;30(6):1162-72. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.20. Epub 2011 Feb 8. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21304489 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis DE-ETIOLATED1 represses photomorphogenesis by positively regulating phytochrome-interacting factors in the dark.Plant Cell. 2014 Sep;26(9):3630-45. doi: 10.1105/tpc.114.130666. Epub 2014 Sep 23. Plant Cell. 2014. PMID: 25248553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ang, L.H., Chattopadhyay, S., Wei, N., Oyama, T., Okada, K., Batschauer, A., and Deng, X.W. (1998). Molecular interaction between COP1 and HY5 defines a regulatory switch for light control of Arabidopsis development. Mol. Cell 1 213–222. - PubMed
-
- Chamovitz, D.A., Wei, N., Osterlund, M.T., von Arnim, A.G., Staub, J.M., Matsui, M., and Deng, X.W. (1996). The COP9 complex, a novel multisubunit nuclear regulator involved in light control of a plant developmental switch. Cell 86 115–121. - PubMed
-
- Chiu, W., Niwa, Y., Zeng, W., Hirano, T., Kobayashi, H., and Sheen, J. (1996). Engineered GFP as a vital reporter in plants. Curr. Biol. 6 325–330. - PubMed
-
- Chory, J., Peto, C., Feinbaum, R., Pratt, L., and Ausubel, F. (1989). Arabidopsis thaliana mutant that develops as a light-grown plant in the absence of light. Cell 58 991–999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

