Tobacco Tsip1, a DnaJ-type Zn finger protein, is recruited to and potentiates Tsi1-mediated transcriptional activation
- PMID: 16844903
- PMCID: PMC1533966
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.106.043158
Tobacco Tsip1, a DnaJ-type Zn finger protein, is recruited to and potentiates Tsi1-mediated transcriptional activation
Abstract
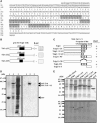
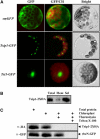
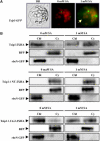
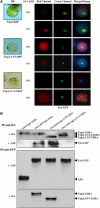
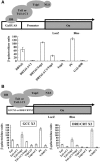
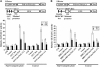
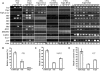
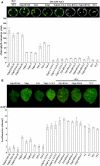
Tobacco stress-induced1 (Tsi1) is an ethylene-responsive-element binding protein/APETALA2-type transcription factor that plays an important role in both biotic and abiotic stress signaling pathways. We show that Tsi1-interacting protein1 (Tsip1), a DnaJ-type Zn finger protein, interacts with Tsi1 in vitro and in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae). The transcript level of Tsip1 in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) increased upon treatment with salicylic acid (SA), ethylene, gibberellic acid, NaCl, and virus challenge. Tsip1 appeared to be physically associated with the chloroplast surface but dissociated from it after SA treatment. Tsip1 colocalized and coimmunoprecipitated with Tsi1 in plant cells following SA treatment. Tsip1 expression increased Tsi1-mediated transcription and was able to functionally compensate for loss of the Tsi1 transcriptional activation domain through a direct interaction with Tsi1. Transgenic plants simultaneously coexpressing Tsi1 and Tsip1 displayed stronger pathogen resistance and salt tolerance than did transgenic plants expressing either Tsi1 or Tsip1 alone. Concurrent with this, the expression of a subset of stress-related genes was induced in a cooperative manner in Tsi1/Tsip1 transgenic plants. These results together implied that Tsi1 recruits Tsip1 to the promoters of stress-related genes to potentiate Tsi1-mediated transcriptional activation.
Figures

References
-
- Banecki, B., Liberek, K., Wall, D., Wawrzynow, A., Georgopoulos, C., Bertoli, E., Tanfani, F., and Zylicz, M. (1996). Structure-function analysis of the zinc finger region of the DnaJ molecular chaperone. J. Biol. Chem. 271 14840–14848. - PubMed
-
- Bauer, J., Chen, K., Hiltbunner, A., Wehrli, E., Eugster, M., Schnell, D., and Kessler, F. (2000). The major protein import receptor of plastids is essential for chloroplast biogenesis. Nature 403 203–207. - PubMed
-
- Braun, D.M., Stone, J.M., and Walker, J.C. (1997). Interaction of the maize and Arabidopsis kinase interaction domains with a subset of receptor-like protein kinases: Implications for transmembrane signals in plants. Plant J. 12 83–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

