HHrep: de novo protein repeat detection and the origin of TIM barrels
- PMID: 16844977
- PMCID: PMC1538828
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl130
HHrep: de novo protein repeat detection and the origin of TIM barrels
Abstract
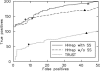
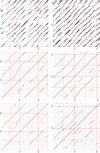
HHrep is a web server for the de novo identification of repeats in protein sequences, which is based on the pairwise comparison of profile hidden Markov models (HMMs). Its main strength is its sensitivity, allowing it to detect highly divergent repeat units in protein sequences whose repeats could as yet only be detected from their structures. Examples include sequences with beta-propellor fold, ferredoxin-like fold, double psi barrels or (betaalpha)8 (TIM) barrels. We illustrate this with proteins from four superfamilies of TIM barrels by revealing a clear 4- and 8-fold symmetry, which we detect solely from their sequences. This symmetry might be the trace of an ancient origin through duplication of a betaalphabetaalpha or betaalpha unit. HHrep can be accessed at http://hhrep.tuebingen.mpg.de.
Figures
Similar articles
-
De novo identification of highly diverged protein repeats by probabilistic consistency.Bioinformatics. 2008 Mar 15;24(6):807-14. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn039. Epub 2008 Feb 1. Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18245125
-
HHsenser: exhaustive transitive profile search using HMM-HMM comparison.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jul 1;34(Web Server issue):W374-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl195. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16845029 Free PMC article.
-
Toward the detection and validation of repeats in protein structure.Proteins. 2004 Nov 1;57(2):365-80. doi: 10.1002/prot.20202. Proteins. 2004. PMID: 15340924
-
Sequence comparison and protein structure prediction.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006 Jun;16(3):374-84. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2006.05.006. Epub 2006 May 19. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006. PMID: 16713709 Review.
-
Evolution, folding, and design of TIM barrels and related proteins.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2021 Jun;68:94-104. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2020.12.007. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2021. PMID: 33453500 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The MPI bioinformatics Toolkit as an integrative platform for advanced protein sequence and structure analysis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jul 8;44(W1):W410-5. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw348. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27131380 Free PMC article.
-
Structural analysis of polarizing indels: an emerging consensus on the root of the tree of life.Biol Direct. 2009 Aug 25;4:30. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-4-30. Biol Direct. 2009. PMID: 19706177 Free PMC article.
-
A galaxy of folds.Protein Sci. 2010 Jan;19(1):124-30. doi: 10.1002/pro.297. Protein Sci. 2010. PMID: 19937658 Free PMC article.
-
Ancient origin of the Parkinson disease gene LRRK2.J Mol Evol. 2008 Jul;67(1):41-50. doi: 10.1007/s00239-008-9122-4. Epub 2008 Jun 4. J Mol Evol. 2008. PMID: 18523712
-
Self-analysis of repeat proteins reveals evolutionarily conserved patterns.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 May 7;21(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-3493-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32381046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Salem G.M., Hutchinson E.G., Orengo C.A., Thornton J.M. Correlation of observed fold frequency with the occurrence of local structural motifs. J. Mol. Biol. 1999;287:969–981. - PubMed
-
- Söding J., Lupas A.N. More than the sum of their parts: on the evolution of proteins from peptides. Bioessays. 2003;25:837–846. - PubMed
-
- Andrade M.A., Ponting C.P., Gibson T.J., Bork P. Homology-based method for identification of protein repeats using statistical significance estimates. J. Mol. Biol. 2000;298:521–537. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

