SWAKK: a web server for detecting positive selection in proteins using a sliding window substitution rate analysis
- PMID: 16845032
- PMCID: PMC1538794
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl272
SWAKK: a web server for detecting positive selection in proteins using a sliding window substitution rate analysis
Abstract
We present a bioinformatic web server (SWAKK) for detecting amino acid sites or regions of a protein under positive selection. It estimates the ratio of non-synonymous to synonymous substitution rates (K(A)/K(S)) between a pair of protein-coding DNA sequences, by sliding a 3D window, or sphere, across one reference structure. The program displays the results on the 3D protein structure. In addition, for comparison or when a reference structure is unavailable, the server can also perform a sliding window analysis on the primary sequence. The SWAKK web server is available at http://oxytricha.princeton.edu/SWAKK/.
Figures
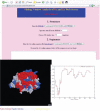
References
-
- Graur D., Li W.H. Fundamentals of Molecular Evolution. 2nd edn. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Press; 2000.
-
- Li W.H., Wu C.I., Luo C.C. A new method for estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous rates of nucleotide substitution considering the relative likelihood of nucleotide and codon changes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1985;2:150–174. - PubMed
-
- Nei M., Gojobori T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1986;3:418–426. - PubMed
-
- Li W.H. Unbiased estimation of the rates of synonymous and nonsynonymous substitution. J. Mol. Evol. 1993;36:96–99. - PubMed
-
- Pamilo P., Bianchi N.O. Evolution of the Zfx and Zfy genes: rates and interdependence between the genes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993;10:271–281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

