Arabidopsis Co-expression Tool (ACT): web server tools for microarray-based gene expression analysis
- PMID: 16845059
- PMCID: PMC1538833
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl204
Arabidopsis Co-expression Tool (ACT): web server tools for microarray-based gene expression analysis
Abstract
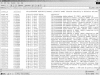
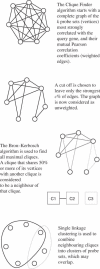
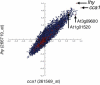
The Arabidopsis Co-expression Tool, ACT, ranks the genes across a large microarray dataset according to how closely their expression follows the expression of a query gene. A database stores pre-calculated co-expression results for approximately 21,800 genes based on data from over 300 arrays. These results can be corroborated by calculation of co-expression results for user-defined sub-sets of arrays or experiments from the NASC/GARNet array dataset. Clique Finder (CF) identifies groups of genes which are consistently co-expressed with each other across a user-defined co-expression list. The parameters can be altered easily to adjust cluster size and the output examined for optimal inclusion of genes with known biological roles. Alternatively, a Scatter Plot tool displays the correlation coefficients for all genes against two user-selected queries on a scatter plot which can be useful for visual identification of clusters of genes with similar r-values. User-input groups of genes can be highlighted on the scatter plots. Inclusion of genes with known biology in sets of genes identified using CF and Scatter Plot tools allows inferences to be made about the roles of the other genes in the set and both tools can therefore be used to generate short lists of genes for further characterization. ACT is freely available at www.Arabidopsis.leeds.ac.uk/ACT.
Figures
References
-
- Rhee S.Y., Beavis W., Berardini T.Z., Chen G.H., Dixon D., Doyle A., Garcia-Hernandez M., Huala E., Lander G., Montoya M., et al. The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): a model organism database providing a centralized, curated gateway to Arabidopsis biology, research materials and community. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:224–228. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Toufighi K., Brady S.M., Austin R., Ly E., Provart N.J. The Botany Array Resource: e-Northerns, Expression Angling, and Promoter analyses. Plant J. 2005;43:153–163. - PubMed
-
- Zimmermann P., Hennig L., Gruissem W. Gene-expression analysis and network discovery using Genevestigator. Trends Plant Sci. 2005;10:407–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

