TICO: a tool for postprocessing the predictions of prokaryotic translation initiation sites
- PMID: 16845076
- PMCID: PMC1538874
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl313
TICO: a tool for postprocessing the predictions of prokaryotic translation initiation sites
Abstract
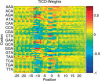
Exact localization of the translation initiation sites (TIS) in prokaryotic genomes is difficult to achieve using conventional gene finders. We recently introduced the program TICO for postprocessing TIS predictions based on a completely unsupervised learning algorithm. The program can be utilized through our web interface at http://tico.gobics.de/ and it is also freely available as a commandline version for Linux and Windows. The latest version of our program provides a tool for visualization of the resulting TIS model. Although the underlying method is not based on any specific assumptions about characteristic sequence features of prokaryotic TIS the prediction rates of our tool are competitive on experimentally verified test data.
Figures

References
-
- Ou H.-Y., Guo F.-B., Zhang C.-T. GS-Finder: a program to find bacterial gene start sites with a self-training method. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004;36:535–544. - PubMed
-
- Zhu H.-Q., Hu G.-Q., Ouyang Z.-Q., Wang J., She Z.-S. Accuracy improvement for identifying translation initiation sites in microbial genomes. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:3308–3317. - PubMed
-
- Tech M., Merkl R. YACOP: enhanced gene prediction obtained by a combination of existing methods. In Silico Biol. 2003;3:441–451. - PubMed
-
- Suzek B.E., Ermolaeva M.D., Schreiber M., Salzberg S.L. A probabilistic method for identifying start codons in bacterial genomes. Bioinformatics. 2001;17:1123–1130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

