Effects of angiotensin II on connexin 43 of VSMCs in arteriosclerosis
- PMID: 16845719
- PMCID: PMC1533757
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.2006.B0648
Effects of angiotensin II on connexin 43 of VSMCs in arteriosclerosis
Abstract
Objective: To observe the effect of angiotensin II (Ang II) on expression of gap junction channel protein connexin 43 (Cx43) in the proliferation process of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) during the early stage of arteriosclerosis.
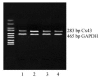
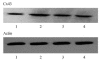
Methods: Thirty-two adult male rabbits were randomly divided into 4 groups. Rabbits in Group A were fed common diet while others in Groups B, C, and D were fed high-cholesterol diet. Losartan (10 mg/(kg.d)) and ramipril (0.5 mg/(kg.d)) were added in the diet of Groups C and D, respectively. The animals were sacrificed after 8 weeks and abdominal aortas were removed and dissected. The expression of Cx43 was assayed using RT-PCR and Western Blotting analysis.
Results: Cx43 was increased markedly in both protein and mRNA level in Groups B, C, and D fed high-cholesterol diet compared with that in control group (P<0.01). Cx43 level in losartan or ramipril treated groups was higher than that in control group (P<0.01, P<0.05), but lower than that in high-cholesterol diet groups (P<0.05, P<0.01).
Conclusion: Cx43 level was upregulated in VSMCs during early atherosclerosis. Losartan and ramipril can inhibit the expression of Cx43.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous