The Diabetes Manual trial protocol - a cluster randomized controlled trial of a self-management intervention for type 2 diabetes [ISRCTN06315411]
- PMID: 16846517
- PMCID: PMC1555586
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2296-7-45
The Diabetes Manual trial protocol - a cluster randomized controlled trial of a self-management intervention for type 2 diabetes [ISRCTN06315411]
Abstract
Background: The Diabetes Manual is a type 2 diabetes self-management programme based upon the clinically effective 'Heart Manual'. The 12 week programme is a complex intervention theoretically underpinned by self-efficacy theory. It is a one to one intervention meeting United Kingdom requirements for structured diabetes-education and is delivered within routine primary care.
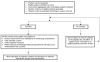
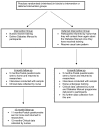
Methods/design: In a two-group cluster randomized controlled trial, GP practices are allocated by computer minimisation to an intervention group or a six-month deferred intervention group. We aim to recruit 250 participants from 50 practices across central England. Eligibility criteria are adults able to undertake the programme with type 2 diabetes, not taking insulin, with HbA1c over 8% (first 12 months) and following an agreed protocol change over 7% (months 13 to 18). Following randomisation, intervention nurses receive two-day training and delivered the Diabetes Manual programme to participants. Deferred intervention nurses receive the training following six-month follow-up. Primary outcome is HbA1c with total and HDL cholesterol; blood pressure, body mass index; self-efficacy and quality of life as additional outcomes. Primary analysis is between-group HbA1c differences at 6 months powered to give 80% power to detect a difference in HbA1c of 0.6%. A 12 month cohort analysis will assess maintenance of effect and assess relationship between self-efficacy and outcomes, and a qualitative study is running alongside.
Discussion: This trial incorporates educational and psychological diabetes interventions into a single programme and assesses both clinical and psychosocial outcomes. The trial will increase our understanding of intervention transferability between conditions, those diabetes related health behaviours that are more or less susceptible to change through efficacy enhancing mechanisms and how this impacts on clinical outcomes.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Foundation International standards for diabetes education 2003 Accessed 14th March 2006 http://www.idf.org/webdata/docs/International%20standards.pdf
-
- Finnish Diabetes Association Development Programme for the Prevention and Care of Diabetes in Finland 2000-2010 http://www.diabetes.fi Accessed 14th March 2006,
-
- DOTA Declaration of the Americas on Diabetes http://www.dota.org/thedeclaration/declaration_e.asp
-
- Department of Health . The expert patient: a new approach to chronic disease management for the 21st century. London , Department of Health; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical