Cross-talk between epidermal growth factor receptor and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha signal pathways increases resistance to apoptosis by up-regulating survivin gene expression
- PMID: 16847054
- PMCID: PMC3132567
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M603414200
Cross-talk between epidermal growth factor receptor and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha signal pathways increases resistance to apoptosis by up-regulating survivin gene expression
Abstract
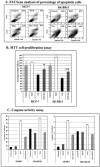
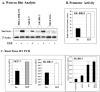
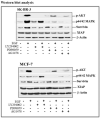
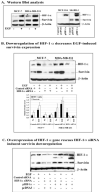
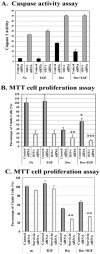
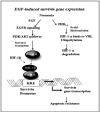
Although increasing evidence supports a link between epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling and resistance to apoptosis, the mechanism by which the EGFR signaling pathway inhibits apoptosis is not well understood. In this study, we found that epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulation increased the level of expression of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein survivin in breast cancer cells but not in normal mammary epithelial cells. We further demonstrated that activation of survivin gene expression is mediated by oxygen-independent hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha up-regulation in EGF-treated cancer cells. EGFR signaling activated the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway, subsequently increasing the level of HIF-1alpha under normoxic conditions. HIF-1alpha then activated survivin gene transcription through direct binding to the survivin promoter. Furthermore, we found that overexpression of HIF-1alpha small interfering RNA blocks EGF-induced survivin gene up-regulation and increases apoptosis induced by the chemotherapy drug docetaxel. However, transfection of a plasmid expressing HIF-1alpha gene activates survivin gene expression and reduces the apoptotic response. Our results demonstrate a novel pathway for EGFR signaling-mediated apoptosis resistance in human cancer cells. Although the role of HIF-1alpha in regulating cell survival under hypoxic conditions has been studied extensively, our results show that normoxic breast cancer cells utilize cross-talk between EGFR signals and HIF-1alpha to up-regulate the anti-apoptotic survivin gene, providing a strong rationale for the targeting of HIF-1alpha as a therapeutic approach for both hypoxic and normoxic tumor cells. Understanding key molecular events in EGFR signaling-induced apoptosis resistance should provide new information for the development of novel therapeutic agents targeting EGFR, HIF-1alpha, and/or survivin.
Figures


References
-
- Danielsen AJ, Maihle NJ. Growth Factors. 2002;20:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Chrysogelos SA, Dickson RB. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1994;29:29–40. - PubMed
-
- Harris AL. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1994;29:1–2. - PubMed
-
- Bucci B, D’Agnano I, Botti C, Mottolese M, Carico E, Zupi G, Vecchione A. Anticancer Res. 1997;17:769–774. - PubMed
-
- Buchholz TA, Tu X, Ang KK, Esteva FJ, Kuerer HM, Pusztai L, Cristofanilli M, Singletary SE, Hortobagyi GN, Sahin AA. Cancer. 2005;104:676–681. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

