FoxA2, Nkx2.2, and PDX-1 regulate islet beta-cell-specific mafA expression through conserved sequences located between base pairs -8118 and -7750 upstream from the transcription start site
- PMID: 16847327
- PMCID: PMC1592775
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00249-06
FoxA2, Nkx2.2, and PDX-1 regulate islet beta-cell-specific mafA expression through conserved sequences located between base pairs -8118 and -7750 upstream from the transcription start site
Abstract
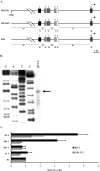
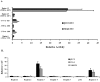
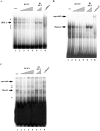
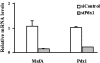
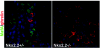
The MafA transcription factor is both critical to islet beta-cell function and has a unique pancreatic cell-type-specific expression pattern. To localize the potential transcriptional regulatory region(s) involved in directing expression to the beta cell, areas of identity within the 5' flanking region of the mouse, human, and rat mafA genes were found between nucleotides -9389 and -9194, -8426 and -8293, -8118 and -7750, -6622 and -6441, -6217 and -6031, and -250 and +56 relative to the transcription start site. The identity between species was greater than 75%, with the highest found between bp -8118 and -7750 ( approximately 94%, termed region 3). Region 3 was the only upstream mammalian conserved region found in chicken mafA (88% identity). In addition, region 3 uniquely displayed beta-cell-specific activity in cell-line-based reporter assays. Important regulators of beta-cell formation and function, PDX-1, FoxA2, and Nkx2.2, were shown to specifically bind to region 3 in vivo using the chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. Mutational and functional analyses demonstrated that FoxA2 (bp -7943 to -7910), Nkx2.2 (bp -7771 to -7746), and PDX-1 (bp -8087 to -8063) mediated region 3 activation. Consistent with a role in transcription, small interfering RNA-mediated knockdown of PDX-1 led to decreased mafA mRNA production in INS-1-derived beta-cell lines (832/13 and 832/3), while MafA expression was undetected in the pancreatic epithelium of Nkx2.2 null animals. These results suggest that beta-cell-type-specific mafA transcription is principally controlled by region 3-acting transcription factors that are essential in the formation of functional beta cells.
Figures


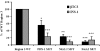
Similar articles
-
Conserved transcriptional regulatory domains of the pdx-1 gene.Mol Endocrinol. 2004 Mar;18(3):533-48. doi: 10.1210/me.2003-0371. Epub 2003 Dec 30. Mol Endocrinol. 2004. PMID: 14701942
-
Characterization of an apparently novel β-cell line-enriched 80-88 kDa transcriptional activator of the MafA and Pdx1 genes.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 8;288(6):3795-803. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.434282. Epub 2012 Dec 26. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23269676 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of PDX-1 in activation of human insulin gene transcription.J Endocrinol. 2006 Feb;188(2):287-94. doi: 10.1677/joe.1.06510. J Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16461554
-
PDX1, Neurogenin-3, and MAFA: critical transcription regulators for beta cell development and regeneration.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Nov 2;8(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0694-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29096722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles and regulation of transcription factor MafA in islet beta-cells.Endocr J. 2007 Dec;54(5):659-66. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.kr-101. Epub 2007 Aug 30. Endocr J. 2007. PMID: 17785922 Review.
Cited by
-
A PDX1-ATF transcriptional complex governs β cell survival during stress.Mol Metab. 2018 Nov;17:39-48. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.07.007. Epub 2018 Aug 1. Mol Metab. 2018. PMID: 30174228 Free PMC article.
-
The MafA transcription factor becomes essential to islet β-cells soon after birth.Diabetes. 2014 Jun;63(6):1994-2005. doi: 10.2337/db13-1001. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24520122 Free PMC article.
-
Proper activation of MafA is required for optimal differentiation and maturation of pancreatic β-cells.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Dec;29(6):821-31. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2015.09.006. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26696512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Foxa2 and MafA regulate islet-specific glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit-related protein gene expression.J Mol Endocrinol. 2008 Nov;41(5):315-28. doi: 10.1677/JME-08-0062. Epub 2008 Aug 27. J Mol Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18753309 Free PMC article.
-
Mnx1: a gatekeeper of β cell fate.Islets. 2012 Jul-Aug;4(4):320-2. doi: 10.4161/isl.21984. Epub 2012 Jul 1. Islets. 2012. PMID: 22935732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Artner, I., J. Le Lay, Y. Hang, L. Elghazi, J. C. Schisler, E. Henderson, B. Sosa-Pineda, and R. Stein. 2006. MafB: an activator of the glucagon gene expressed in developing islet {alpha}- and {beta}-cells. Diabetes 55:297-304. - PubMed
-
- Ashery-Padan, R., X. Zhou, T. Marquardt, P. Herrera, L. Toube, A. Berry, and P. Gruss. 2004. Conditional inactivation of Pax6 in the pancreas causes early onset of diabetes. Dev. Biol. 269:479-488. - PubMed
-
- Bain, J. R., J. C. Schisler, K. Takeuchi, C. B. Newgard, and T. C. Becker. 2004. An adenovirus vector for efficient RNA interference-mediated suppression of target genes in insulinoma cells and pancreatic islets of langerhans. Diabetes 53:2190-2194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
