Role of the Cldn6 cytoplasmic tail domain in membrane targeting and epidermal differentiation in vivo
- PMID: 16847338
- PMCID: PMC1592757
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.02342-05
Role of the Cldn6 cytoplasmic tail domain in membrane targeting and epidermal differentiation in vivo
Abstract
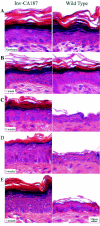
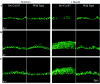
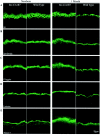
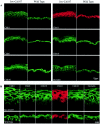
It is widely recognized that the claudin (Cldn) family of four tetraspan transmembrane proteins is crucial for tight junction assembly and permeability barrier function; however, the precise role of the tail and loop domains in Cldn function is not understood. We hypothesized that the cytoplasmic tail domain of Cldn6 is crucial for membrane targeting and hence epidermal permeability barrier (EPB) formation. To test this hypothesis via a structure-function approach, we generated a tail deletion of Cldn6 (CDelta187) and evaluated its role in epidermal differentiation and EPB formation through its forced expression via the involucrin (Inv) promoter in the suprabasal compartment of the transgenic mouse epidermis. Even though a functional barrier formed, Inv-CDelta187 mice displayed histological and biochemical abnormalities in the epidermal differentiation program and stimulation of epidermal cell proliferation in both the basal and suprabasal compartments of the interfolliclar epidermis, leading to a thickening of the epidermis after 1 week of age that persisted throughout life. Although some membrane localization was evident, our studies also revealed a significant amount of not only Cldn6 but also Cldn10, Cldn11, and Cldn18 in the cytoplasm of transgenic epidermal cells as well as the activation of a protein-unfolding pathway. These findings demonstrate that the overexpression of a tail truncation mutant of Cldn6 mislocalizes Cldn6 and other Cldn proteins to the cytoplasm and triggers a postnatal increase in proliferation and aberrant differentiation of the epidermis, emphasizing the importance of the Cldn tail domain in membrane targeting and function in vivo.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The targeted overexpression of a Claudin mutant in the epidermis of transgenic mice elicits striking epidermal and hair follicle abnormalities.Mol Biotechnol. 2007 Jun;36(2):166-74. doi: 10.1007/s12033-007-0027-z. Mol Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17914196
-
Involucrin-claudin-6 tail deletion mutant (CDelta206) transgenic mice: a model of delayed epidermal permeability barrier formation and repair.Dis Model Mech. 2010 Mar-Apr;3(3-4):167-80. doi: 10.1242/dmm.002634. Epub 2010 Jan 27. Dis Model Mech. 2010. PMID: 20106878
-
Delayed epidermal permeability barrier formation and hair follicle aberrations in Inv-Cldn6 mice.Mech Dev. 2005 Jun;122(6):805-19. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2005.03.001. Epub 2005 Apr 21. Mech Dev. 2005. PMID: 15908185
-
CLDN6: From Traditional Barrier Function to Emerging Roles in Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 14;22(24):13416. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413416. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Claudin 6: Therapeutic prospects for tumours, and mechanisms of expression and regulation (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2021 Sep;24(3):677. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12316. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34296304 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The targeted overexpression of a Claudin mutant in the epidermis of transgenic mice elicits striking epidermal and hair follicle abnormalities.Mol Biotechnol. 2007 Jun;36(2):166-74. doi: 10.1007/s12033-007-0027-z. Mol Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17914196
-
Biophysics of claudin proteins in tight junction architecture: Three decades of progress.Biophys J. 2024 Aug 20;123(16):2363-2378. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.06.010. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Biophys J. 2024. PMID: 38859584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic significance of claudin-1 and cyclin B1 protein expression in patients with hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2016 May;11(5):2995-3002. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4333. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27123052 Free PMC article.
-
Transgene-mediated rescue of spermatogenesis in Cldn11-null mice.Biol Reprod. 2012 May 3;86(5):139, 1-11. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.111.096230. Print 2012 May. Biol Reprod. 2012. PMID: 22378758 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the distribution pattern of Claudin tight junction proteins during the progression of mouse skin tumorigenesis.BMC Cancer. 2007 Oct 18;7:196. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-196. BMC Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17945025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balkovetz, D. F. 2006. Claudins at the gate: determinants of renal epithelial tight junction paracellular permeability. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 290:F572-F579. - PubMed
-
- Barnard, N. J., P. A. Hall, N. R. Lemoine, and N. Kadar. 1987. Proliferative index in breast carcinoma determined in situ by Ki67 immunostaining and its relationship to clinical and pathological variables. J. Pathol. 152:287-295. - PubMed
-
- Berditchevski, F., E. Odintsova, S. Sawada, and E. Gilbert. 2002. Expression of the palmitoylation-deficient CD151 weakens the association of alpha 3 beta 1 integrin with the tetraspanin-enriched microdomains and affects integrin-dependent signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 277:36991-37000. - PubMed
-
- Candi, E., R. Schmidt, and G. Melino. 2005. The cornified envelope: a model of cell death in the skin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6:328-340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
