Understanding the molecular basis of the interaction between NDPK-A and AMPK alpha 1
- PMID: 16847342
- PMCID: PMC1592779
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00315-06
Understanding the molecular basis of the interaction between NDPK-A and AMPK alpha 1
Retraction in
-
Understanding the molecular basis of the interaction between NDPK-A and AMPK alpha1.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Sep;28(18):5827. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00859-08. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18772271 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
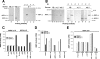
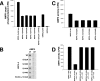
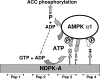
Nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK) (nm23/awd) belongs to a multifunctional family of highly conserved proteins (approximately 16 to 20 kDa) including two well-characterized isoforms (NDPK-A and -B). NDPK catalyzes the conversion of nucleoside diphosphates to nucleoside triphosphates, regulates a diverse array of cellular events, and can act as a protein histidine kinase. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a heterotrimeric protein complex that responds to the cellular energy status by switching off ATP-consuming pathways and switching on ATP-generating pathways when ATP is limiting. AMPK was first discovered as an activity that inhibited preparations of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase 1 (ACC1), a regulator of cellular fatty acid synthesis. We recently reported that NDPK-A (but not NDPK-B) selectively regulates the alpha1 isoform of AMPK independently of the AMP concentration such that the manipulation of NDPK-A nucleotide trans-phosphorylation activity to generate ATP enhanced the activity of AMPK. This regulation occurred irrespective of the surrounding ATP concentration, suggesting that "substrate channeling" was occurring with the shielding of NDPK-generated ATP from the surrounding medium. We speculated that AMPK alpha1 phosphorylated NDPK-A during their interaction, and here, we identify two residues on NDPK-A targeted by AMPK alpha1 in vivo. We find that NDPK-A S122 and S144 are phosphorylated by AMPK alpha1 and that the phosphorylation status of S122, but not S144, determines whether substrate channeling can occur. We report the cellular effects of the S122 mutation on ACC1 phosphorylation and demonstrate that the presence of E124 (absent in NDPK-B) is necessary and sufficient to permit both AMPK alpha1 binding and substrate channeling.
Figures
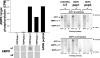


Similar articles
-
A novel physical and functional association between nucleoside diphosphate kinase A and AMP-activated protein kinase alpha1 in liver and lung.Biochem J. 2005 Nov 15;392(Pt 1):201-9. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050269. Biochem J. 2005. Retraction in: Biochem J. 2009 Feb 1;417(3):813. doi: 10.1042/bj4170813. PMID: 16026327 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Protein kinase CK2 acts as a signal molecule switching between the NDPK-A/AMPK alpha1 complex and NDPK-B.FASEB J. 2007 Jan;21(1):88-98. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-6804com. Epub 2006 Nov 29. FASEB J. 2007. Retraction in: FASEB J. 2007 Oct;21(12):3398. PMID: 17135357 Retracted.
-
NDPK-A (but not NDPK-B) and AMPK alpha1 (but not AMPK alpha2) bind the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in epithelial cell membranes.Cell Signal. 2006 Oct;18(10):1595-603. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.01.001. Epub 2006 Feb 8. Cell Signal. 2006. PMID: 16466905
-
Nucleoside diphosphate kinase A as a controller of AMP-kinase in airway epithelia.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2006 Aug;38(3-4):181-7. doi: 10.1007/s10863-006-9033-2. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2006. PMID: 17039396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of fatty acid synthesis and oxidation by the AMP-activated protein kinase.Biochem Soc Trans. 2002 Nov;30(Pt 6):1064-70. doi: 10.1042/bst0301064. Biochem Soc Trans. 2002. PMID: 12440973 Review.
Cited by
-
The cystic fibrosis transmembrane recruiter the alter ego of CFTR as a multi-kinase anchor.Pflugers Arch. 2007 Nov;455(2):215-21. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0290-7. Epub 2007 Sep 6. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17805562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AMPK directly inhibits NDPK through a phosphoserine switch to maintain cellular homeostasis.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Jan;23(2):381-9. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-08-0699. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22114351 Free PMC article.
-
The ubiquitin E3 ligase SCF-FBXO24 recognizes deacetylated nucleoside diphosphate kinase A to enhance its degradation.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Mar;35(6):1001-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01185-14. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25582197 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of AMPKalpha1 Ameliorates Fatty Liver in Hyperlipidemic Diabetic Rats.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009 Dec;13(6):449-54. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2009.13.6.449. Epub 2009 Dec 31. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 20054491 Free PMC article.
-
Dual functions of NME1 in suppression of cell motility and enhancement of genomic stability in melanoma.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015 Feb;388(2):199-206. doi: 10.1007/s00210-014-1010-4. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25017017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnaud-Dabernat, S., P. M. Bourbon, A. Dierich, M. Le Meur, and J. Y. Daniel. 2003. Knockout mice as model systems for studying nm23/NDP kinase gene functions. Application to the nm23-M1 gene. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 35:19-30. - PubMed
-
- Biondi, R. M., M. Engel, M. Sauane, C. Welter, O. G. Issinger, L. Jimenez de Asua, and S. Passeron. 1996. Inhibition of nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity by in vitro phosphorylation by protein kinase CK2. Differential phosphorylation of NDP kinases in HeLa cells in culture. FEBS Lett. 399:183-187. - PubMed
-
- Bosnar, M. H., J. De Gunzburg, R. Bago, L. Brecevic, I. Weber, and J. Pavelic. 2004. Subcellular localization of A and B Nm23/NDPK subunits. Exp. Cell Res. 298:275-284. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
-
- Caligo, M. A., G. Cipollini, L. Fiore, S. Calvo, F. Basolo, P. Collecchi, F. Ciardiello, S. Pepe, M. Petrini, and G. Bevilacqua. 1995. NM23 gene expression correlates with cell growth rate and S-phase. Int. J. Cancer 60:837-842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
