Suspected clindamycin-associated oesophageal injury in cats: five cases
- PMID: 16849039
- PMCID: PMC10832923
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jfms.2006.04.006
Suspected clindamycin-associated oesophageal injury in cats: five cases
Abstract
The clinical findings, treatment and outcome of suspected clindamycin-associated oesophageal injury in five cats are reported. All cats were treated with one 75 mg clindamycin capsule twice daily (dose range 12-19 mg/kg). Capsules were administered without food or a water bolus. Dysphagia, regurgitation, choking or gagging were seen 3-9 days after starting clindamycin. On oesophagoscopy, three cats had oesophagitis, one of which progressed to stricture formation. Two cats had an oesophageal stricture at first presentation. This is the first report of suspected clindamycin-associated oesophageal injury in cats. It serves to further alert practitioners to the potential for drug-induced oesophageal disorders (DIOD) in cats treated with oral medications and to urge prevention by promoting a change in dosing practices.
Figures
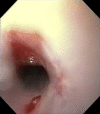
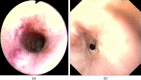
Similar articles
-
Oesophageal stricture in cats associated with use of the hyclate (hydrochloride) salt of doxycycline.J Feline Med Surg. 2005 Aug;7(4):241-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jfms.2005.05.002. J Feline Med Surg. 2005. PMID: 16055011 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Oesophageal strictures in cats associated with doxycycline therapy.J Feline Med Surg. 2005 Feb;7(1):33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jfms.2004.04.001. J Feline Med Surg. 2005. PMID: 15686972 Free PMC article.
-
Oesophageal stricture in a cat due to oral administration of tetracyclines.J Small Anim Pract. 2002 May;43(5):221-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-5827.2002.tb00062.x. J Small Anim Pract. 2002. PMID: 12038856
-
Clindamycin in dentistry.J Dent Assoc S Afr. 1994 Nov;49(11):563-6. J Dent Assoc S Afr. 1994. PMID: 9508961 Review.
-
Anaerobic infections in small animals.Probl Vet Med. 1990 Jun;2(2):330-47. Probl Vet Med. 1990. PMID: 2134596 Review.
Cited by
-
A One Health review of aerodigestive disease in dogs.J Vet Intern Med. 2023 May-Jun;37(3):817-834. doi: 10.1111/jvim.16661. Epub 2023 Mar 28. J Vet Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 36987535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute vomiting in cats: rational treatment selection.J Feline Med Surg. 2010 Mar;12(3):225-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jfms.2010.01.005. J Feline Med Surg. 2010. PMID: 20193913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospective evaluation of an indwelling esophageal balloon dilatation feeding tube for treatment of benign esophageal strictures in dogs and cats.J Vet Intern Med. 2018 Mar;32(2):693-700. doi: 10.1111/jvim.15071. Epub 2018 Feb 20. J Vet Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 29460330 Free PMC article.
-
Transient megaoesophagus and oesophagitis following diaphragmatic rupture repair in a cat.J Feline Med Surg. 2008 Jul;10(3):284-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jfms.2007.11.001. Epub 2008 Feb 4. J Feline Med Surg. 2008. PMID: 18243747 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery of normal esophageal function in a kitten with diffuse megaesophagus and an occult lower esophageal stricture.J Feline Med Surg. 2015 Jun;17(6):557-61. doi: 10.1177/1098612X14542451. Epub 2014 Jul 16. J Feline Med Surg. 2015. PMID: 25030954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson K.D., Rouse T.M., Randolph J.G. A controlled trial of corticosteroids in children with corrosive injury of the esophagus, New England Journal of Medicine 323, 1990, 637–640. - PubMed
-
- Baskin D., Urganci N., Abbasoglu L., Alkim C., Yalcin M., Karadag C., Sever N. A standardised protocol for the acute management of corrosive ingestion in children, Pediatric Surgery International 20, 2004, 824–828. - PubMed
-
- Bokey L., Hugh T.B. Oesophageal ulceration associated with doxycycline therapy, Medical Journal of Australia 1, 1975, 236–237. - PubMed
-
- Boyce H.W. Drug-induced esophageal damage: diseases of medical progress, Gastrointestinal Endoscopy 47, 1998, 547–550. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

