In vitro and in vivo biological responses to a novel radiopacifying agent for bone cement
- PMID: 16849166
- PMCID: PMC1578263
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2004.0009
In vitro and in vivo biological responses to a novel radiopacifying agent for bone cement
Abstract
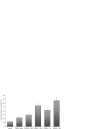
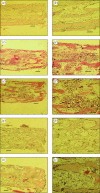
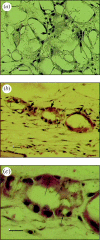
Iodixanol (IDX) and iohexol (IHX) have been investigated as possible radiopacification agents for polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) bone cement, to replace the currently used barium sulphate and zirconia. IDX and IHX are both water-soluble iodine-based contrast media and for the last 20 years have been used extensively in clinical diagnostic procedures such as contrast media enhanced computed tomography, angiography and urography. One of the major reasons to remove the current radiopacifying agents is their well-documented cytotoxicity and their potential to increase bone resorption. Using in vitro bone resorption assays, the effect of PMMA particles plus IDX or IHX to induce osteoclast formation and lacunar resorption on dentine slices has been investigated. These responses have been compared with the in vitro response to PMMA particles containing the conventional radiopacifying agents, that is, barium sulphate and zirconia. In parallel, the in vivo reaction, in terms of new bone formation, to particles of these materials has been tested using a bone harvest chamber in rabbit tibiae. In vitro cell culture showed that PMMA containing IHX resulted in significantly less bone resorption than PMMA containing the conventional opacifiers. In vivo testing, however, showed no significant differences between the amounts of new bone formed around cement samples containing the two iodine-based opacifying agents in particulate form, although both led to fewer inflammatory cells than particles of PMMA containing zirconia. Our results suggest that a non-ionic radiopacifier could be considered as an alternative to the conventional radiopacifying agents used in biomaterials in orthopaedic surgery.
Figures

References
-
- Almén T. Visipaque—a step forward. A historical review. Acta Radiol. Suppl. 1995;399:2–18. - PubMed
-
- Artola A, Gurruchaga M, Vázquez B, San Roman J, Goñi I. Elimination of barium sulphate from acrylic bone cements. Use of two iodine containing monomers. Biomaterials. 2004;24:4071–4080. - PubMed
-
- Aspenberg P, van der Vis H. Migration, particles, and fluid pressure. A discussion of causes of prosthetic loosening. Clin. Orthop. Rel. Res. 1998;352:75–80. - PubMed
-
- Aspenberg P, Albrektsson T, Lohmander L.S, Thorngren K.G. Drug test chamber: a titanium implant for administration of biochemical agents to a standardized bone callus in situ. J. Biomed. Eng. 1988;10:70–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
