Calcium-binding phospholipids as a coating material for implant osteointegration
- PMID: 16849237
- PMCID: PMC1578739
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2005.0088
Calcium-binding phospholipids as a coating material for implant osteointegration
Abstract
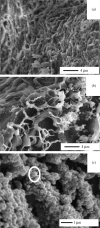
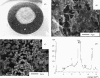
Among the many biomolecules involved in the bone mineralization processes, anionic phospholipids play an important role because of their ability to bind calcium. In particular, phosphatidylserine is a natural component of the plasmalemma and of the matrix vesicles generated from the osteoblast membrane to create nucleation centres for calcium phosphate crystal precipitation. In the present work, we demonstrate that calcium-binding phospholipids can be used as biomimetic coating materials for improving the osteointegration of metal implants. Relatively thick phosphatidylserine-based coatings were deposited on titanium coupons by dip-coating. Upon dehydration in a simulated body fluid phospholipids were quickly crosslinked by calcium and re-arranged into a three-dimensional matrix able to induce rapid formation of a calcium phosphate mineral phase. The rate of mineralization was shown to be dependent on the adopted coating formulation. In the attempt to closely mimic the cell membrane composition, heterogeneous formulations based on the mixing of anionic phospholipids (either phosphatidylserine or phosphatidylinositol) with phosphatidylcholine and cholesterol were synthesized. However, surface plasmon resonance studies as well as scanning electron microscopy and elemental analysis demonstrated that the homogeneous phosphatidylserine coating was a more effective calcification environment than the heterogeneous formulations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In vivo comparison of bone formation on titanium implant surfaces coated with biomimetically deposited calcium phosphate or electrochemically deposited hydroxyapatite.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010 Jul-Aug;25(4):669-80. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010. PMID: 20657861
-
Nano-scale study of the nucleation and growth of calcium phosphate coating on titanium implants.Biomaterials. 2004 Jun;25(14):2901-10. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.09.063. Biomaterials. 2004. PMID: 14962569
-
[Preparation of hydroxyapatite coating in concentrated simulated body fluid by accelerated biomimetic synthesis].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2007 Dec;24(6):1314-8. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 18232484 Chinese.
-
Structural influence from calcium phosphate coatings and its possible effect on enhanced bone integration.Acta Odontol Scand. 2009;67(6):333-40. doi: 10.1080/00016350903188325. Acta Odontol Scand. 2009. PMID: 19722110 Review.
-
Osteoinductive implants: the mise-en-scène for drug-bearing biomimetic coatings.Ann Biomed Eng. 2004 Mar;32(3):398-406. doi: 10.1023/b:abme.0000017536.10767.0f. Ann Biomed Eng. 2004. PMID: 15095814 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of polyelectrolyte adsorption on lateral distribution and dynamics of anionic lipids: a Monte Carlo study of a coarse-grain model.Eur Biophys J. 2014 Sep;43(8-9):377-91. doi: 10.1007/s00249-014-0969-6. Epub 2014 Jun 28. Eur Biophys J. 2014. PMID: 24972687
-
Osseointegration of titanium implants functionalised with phosphoserine-tethered poly(epsilon-lysine) dendrons: a comparative study with traditional surface treatments in sheep.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015 Feb;26(2):87. doi: 10.1007/s10856-015-5433-3. Epub 2015 Feb 3. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015. PMID: 25644101
-
Osteoconductive phosphoserine-modified poly({varepsilon}-lysine) dendrons: synthesis, titanium oxide surface functionalization and response of osteoblast-like cell lines.J R Soc Interface. 2013 Feb;10(79):20120765. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2012.0765. J R Soc Interface. 2013. PMID: 23193106 Free PMC article.
-
Role of phosphatidyl-serine in bone repair and its technological exploitation.Molecules. 2009 Dec 22;14(12):5367-81. doi: 10.3390/molecules14125367. Molecules. 2009. PMID: 20032899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Compositional redistribution and dynamic heterogeneity in mixed lipid membrane induced by polyelectrolyte adsorption: effects of chain rigidity.Eur Phys J E Soft Matter. 2014 Aug;37(8):27. doi: 10.1140/epje/i2014-14071-8. Epub 2014 Aug 22. Eur Phys J E Soft Matter. 2014. PMID: 25143187
References
-
- Bigi A, Foresti E, Gregorini R, Ripamonti A, Roveri N, Shah J.S. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1992;50:439–444. doi:10.1007/BF00296775 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eanes E. Bone Miner. 1992;17:269–272. doi:10.1016/0169-6009(92)90749-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eanes E.D, Hailer A.W. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1985;37:390–394. - PubMed
-
- Eanes E.D, Hailer A.W, Midura R.J, Hascall V.C. Glycobiology. 1992;2:571–578. - PubMed
-
- Habibovic P, Barrere F, van Blitterswijk C.A, De Groot K, Layrolle P. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2002;85:517–522.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

