A randomized control trial of Internet-delivered HIV prevention targeting rural MSM
- PMID: 16849391
- PMCID: PMC2639555
- DOI: 10.1093/her/cyl057
A randomized control trial of Internet-delivered HIV prevention targeting rural MSM
Abstract
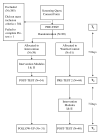
The Internet may be important for delivering human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) risk reduction to men who have sex with men (MSM) in rural areas. This randomized control trial (RCT) tested the acceptability and efficacy of an Internet-delivered HIV risk-reduction intervention. Two modules include a conversation between an HIV-negative man and an HIV-positive man, with interactive graphics. Ninety men were randomly assigned to intervention or wait-list control and 79% completed the study. An 'intent-to-treat' model was used. HIV/acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) knowledge, self-efficacy and outcome expectancies increased after participating in the intervention, and changes were maintained at 1-week follow-up. Participants said they would participate again. This RCT provides support for the acceptability and efficacy of the Internet for delivering HIV prevention messages to rural MSM.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- CDC. HIV Surveillance Report, 2002. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2002.
-
- Preston DB, D'Aguelli AR, Kassab CD, et al. The influence of stigma on the sexual risk behavior of rural men who have sex with men. AIDS Educ Prev. 2004;16:291–303. - PubMed
-
- Madden M, Rainie L. America's Online Pursuits: The Changing Picture of Who's Online and What They Do. Washington, DC: PEW Internet and American Life Project; 2003.
-
- Cooper A. Sexuality and the Internet: surfing into the new millennium. Cyberpsychol Behav. 1998;1:187–93.
-
- Horvath K, Bowen A, Williams M. Virtual and physical venues as contexts for HIV-risk behaviors among rural men who have sex with men. Health Psychol. 2006;25:237–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical