Topoisomerase IIIalpha and Bloom's helicase can resolve a mobile double Holliday junction substrate through convergent branch migration
- PMID: 16849422
- PMCID: PMC1544052
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0604873103
Topoisomerase IIIalpha and Bloom's helicase can resolve a mobile double Holliday junction substrate through convergent branch migration
Abstract
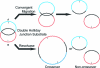
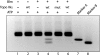
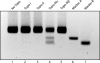
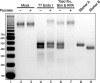
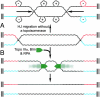
It has long been suspected that a double Holliday junction (dHJ) could be resolved by a topoisomerase partnered with a helicase by convergent branch migration of the HJs. Genetic analysis of yeast TOP3 and SGS1 has lent considerable evidence to the notion that the protein products of these genes are involved in just such a process, although biochemical analysis of the metabolism of a dHJ has been hindered by the lack of a substrate that adequately replicates the endogenous structure. We have synthesized a dHJ substrate that recapitulates many of the features of an endogenous dHJ and represents a much earlier intermediate in the resolution pathway. Here, we show that Drosophila topoisomerase IIIalpha (Topo IIIalpha) and Blm (a homolog of Sgs1) are capable of resolving this substrate to non-cross-over products and that this activity is stimulated by replication protein A (RPA). We investigated the ability of other Drosophila topoisomerases to perform this reaction in concert with Blm and RPA and discovered that this resolution activity is unique to Topo IIIalpha. Examination of the mechanism of resolution reveals that Topo IIIalpha, Blm, and RPA resolve this substrate by convergent migration of the two HJs toward each other, collapsing the dHJ. This mechanism stands in contrast to classic resolvase activities that use a structure-specific endonuclease to cleave the HJs.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Holliday junction processing activity of the BLM-Topo IIIalpha-BLAP75 complex.J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 26;282(43):31484-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M706116200. Epub 2007 Aug 28. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17728255
-
A double Holliday junction dissolvasome comprising BLM, topoisomerase IIIalpha, and BLAP75.J Biol Chem. 2006 May 19;281(20):13861-4. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C600051200. Epub 2006 Apr 4. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16595695
-
Role of replication protein A in double holliday junction dissolution mediated by the BLM-Topo IIIα-RMI1-RMI2 protein complex.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 17;288(20):14221-14227. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.465609. Epub 2013 Mar 30. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23543748 Free PMC article.
-
The dissolution of double Holliday junctions.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Jul 1;6(7):a016477. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016477. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 24984776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
When helicase and topoisomerase meet!J Cell Sci. 1997 Jun;110 ( Pt 12):1345-50. doi: 10.1242/jcs.110.12.1345. J Cell Sci. 1997. PMID: 9217320 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome instability and embryonic developmental defects in RMI1 deficient mice.DNA Repair (Amst). 2013 Oct;12(10):835-43. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2013.07.004. Epub 2013 Jul 27. DNA Repair (Amst). 2013. PMID: 23900276 Free PMC article.
-
Structural mechanisms of human RecQ helicases WRN and BLM.Front Genet. 2014 Oct 29;5:366. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00366. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 25400656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meiotic Crossover Patterning.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 22;9:681123. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.681123. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34368131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Top3-Rmi1 DNA single-strand decatenase is integral to the formation and resolution of meiotic recombination intermediates.Mol Cell. 2015 Feb 19;57(4):583-594. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.020. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25699707 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple functions of Drosophila BLM helicase in maintenance of genome stability.Genetics. 2007 Aug;176(4):1979-92. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.070052. Epub 2007 May 16. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17507683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heyer W. D. Curr. Biol. 2004;14:R56–R58. - PubMed
-
- Heyer W. D., Ehmsen K. T., Solinger J. A. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003;28:548–557. - PubMed
-
- Symington L. S., Holloman W. K. Science. 2004;303:184–185. - PubMed
-
- Nasmyth K. A. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1982;16:439–500. - PubMed
-
- Wang J. C. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002;3:430–440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

