Autoimmunity as a result of escape from RNA surveillance
- PMID: 16849479
- PMCID: PMC2206679
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.3.1698
Autoimmunity as a result of escape from RNA surveillance
Abstract
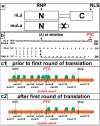
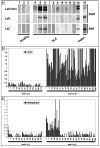
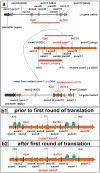
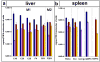
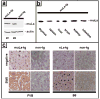
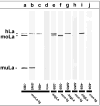
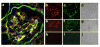
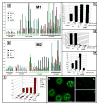
In previous studies, we detected a frame shift mutation in the gene encoding the autoantigen La of a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. The mutant La mRNA contains a premature termination codon. mRNAs that prematurely terminate translation should be eliminated by RNA quality control mechanisms. As we find Abs specific for the mutant La form in approximately 30% of sera from anti-La-positive patients, we expected that mutant La mRNAs circumvent RNA control and the expression of mutant La protein could become harmful. Indeed, real-time PCR, immunostaining, and immunoblotting data of mice transgenic for the mutant La form show that mutant La mRNAs are not repressed in these animals and are translated to mutant La protein. In addition to the mutant La protein, we detected a minor portion of native human La in the mutant La-transgenic mice. Therefore, ribosomal frame shifting may allow the mutant La mRNA to escape from RNA control. Interestingly, expression of the mutant La mRNA results in a lupus-like disease in the experimental mice. Consequently, escape of mutant La mRNA from RNA control can have two effects: it 1) results in the expression of an immunogenic (neo)epitope, and 2) predisposes to autoimmunity.
Figures
References
-
- Fasken MB, Corbett HA. Process or perish: quality control in mRNA biogenesis. Nature Struct Biol. 2005;12:482–489. - PubMed
-
- Weischenfeldt J, Lykke-Andersen J, Porse B. Messenger RNA Surveillance: Neutralizing Natural Nonsense. Current Biol. 2005;15:R559–R562. - PubMed
-
- Culbertson MR. RNA surveillance: unforeseen consequences for gene expression, inherited genetic disorders and cancer. Trends Genet. 1999;15:74–80. - PubMed
-
- Hentze MW, Kulozik AE. A perfect message: RNA surveillance and nonsense-mediated decay. Cell. 1999;96:307–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI054117/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR049084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE015223/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R41 AI054117/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR020143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AR42460/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI48097/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- IP20RR15577/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI031584/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015577/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR020143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI24717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM063497/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042460/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI131584/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- GM63497/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DE015223/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AR048940/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI048097/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI51647/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI053747/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007633/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI053747/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR48940/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AR049084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K02 AI051647/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

