An efficient genetic screen in Drosophila to identify nuclear-encoded genes with mitochondrial function
- PMID: 16849596
- PMCID: PMC1569793
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.061705
An efficient genetic screen in Drosophila to identify nuclear-encoded genes with mitochondrial function
Abstract
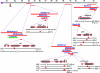
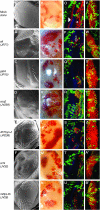
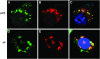
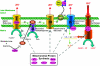
We conducted a screen for glossy-eye flies that fail to incorporate BrdU in the third larval instar eye disc but exhibit normal neuronal differentiation and isolated 23 complementation groups of mutants. These same phenotypes were previously seen in mutants for cytochrome c oxidase subunit Va. We have molecularly characterized six complementation groups and, surprisingly, each encodes a mitochondrial protein. Therefore, we believe our screen to be an efficient method for identifying genes with mitochondrial function.
Figures

References
-
- Ackerman, S. H., and A. Tzagoloff, 2005. Function, structure, and biogenesis of mitochondrial ATP synthase. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 80: 95–133. - PubMed
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers and D. J. Lipman, 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: 403–410. - PubMed
-
- Ashby, M. N., S. Y. Kutsunai, S. Ackerman, A. Tzagoloff and P. A. Edwards, 1992. COQ2 is a candidate for the structural gene encoding para-hydroxybenzoate:polyprenyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 4128–4136. - PubMed
-
- Boyer, P. D., 1997. The ATP synthase: a splendid molecular machine. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 66: 717–749. - PubMed
-
- Claros, M. G., and P. Vincens, 1996. Computational method to predict mitochondrially imported proteins and their targeting sequences. Eur. J. Biochem. 241: 779–786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

