The maize Ab10 meiotic drive system maps to supernumerary sequences in a large complex haplotype
- PMID: 16849609
- PMCID: PMC1569779
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.105.048322
The maize Ab10 meiotic drive system maps to supernumerary sequences in a large complex haplotype
Abstract
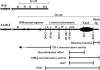
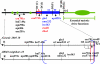
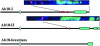
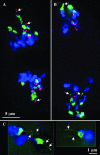
The meiotic drive system on maize abnormal chromosome 10 (Ab10) is contained within a terminal domain of chromatin that extends the long arm of Ab10 to approximately 1.3 times the size of normal chromosome 10L. Ab10 type I (Ab10-I) does not recombine with normal chromosome 10 (N10) over an approximately 32-cM terminal region of the long arm. Comparative RFLP mapping demonstrates that multiple independent rearrangements are responsible for the current organization of Ab10-I, including a set of nested inversions and at least one long supernumerary segment at the end of the chromosome. Four major meiotic drive functions, i.e., the recombination effect, smd3, 180-bp neocentromere activity, and the distal tip function, all map to the distal supernumerary segment. TR-1-mediated neocentromere activity (the fifth known drive function) is nonessential in the type II variant of Ab10 and maps to a central region that may include a second supernumerary insertion. Both neocentromere activity and the recombination effect behave as dominant gain-of-function mutations, consistent with the view that meiotic drive involves new or alien gene products. These and other data suggest that the Ab10 meiotic drive system was initially acquired from a related species and that a complex haplotype evolved around it.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Four loci on abnormal chromosome 10 contribute to meiotic drive in maize.Genetics. 2003 Jun;164(2):699-709. doi: 10.1093/genetics/164.2.699. Genetics. 2003. PMID: 12807790 Free PMC article.
-
Conflicting Kinesin-14s in a single chromosomal drive haplotype.Genetics. 2025 Jul 9;230(3):iyaf091. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyaf091. Genetics. 2025. PMID: 40365704
-
Fitness Costs and Variation in Transmission Distortion Associated with the Abnormal Chromosome 10 Meiotic Drive System in Maize.Genetics. 2018 Jan;208(1):297-305. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300060. Epub 2017 Nov 9. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29122827 Free PMC article.
-
The maize abnormal chromosome 10 meiotic drive haplotype: a review.Chromosome Res. 2022 Sep;30(2-3):205-216. doi: 10.1007/s10577-022-09693-6. Epub 2022 Jun 2. Chromosome Res. 2022. PMID: 35652970 Review.
-
Mixed knobs in corn cobs.Genes Dev. 2020 Sep 1;34(17-18):1110-1112. doi: 10.1101/gad.343350.120. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 32873577 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diversity and abundance of the abnormal chromosome 10 meiotic drive complex in Zea mays.Heredity (Edinb). 2013 Jun;110(6):570-7. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2013.2. Epub 2013 Feb 27. Heredity (Edinb). 2013. PMID: 23443059 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution and biology of supernumerary B chromosomes.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Feb;71(3):467-78. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1437-7. Epub 2013 Aug 3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 23912901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The maize striate leaves2 (sr2) gene encodes a conserved DUF3732 domain and is homologous to the rice yss1 gene.Plant Direct. 2024 Feb 13;8(2):e567. doi: 10.1002/pld3.567. eCollection 2024 Feb. Plant Direct. 2024. PMID: 38357415 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic drive of female-inherited supernumerary chromosomes in a pathogenic fungus.Elife. 2018 Dec 13;7:e40251. doi: 10.7554/eLife.40251. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30543518 Free PMC article.
-
Centromeres: long intergenic spaces with adaptive features.Funct Integr Genomics. 2009 Aug;9(3):287-92. doi: 10.1007/s10142-009-0124-0. Epub 2009 May 12. Funct Integr Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19434433 Review.
References
-
- Ardlie, K. G., 1998. Putting the brake on drive: meiotic drive of t haplotypes in natural populations of mice. Trends Genet. 14: 189–193. - PubMed
-
- Bernasconi, G., T. L. Ashman, T. R. Birkhead, J. D. Bishop, U. Grossniklaus et al., 2004. Evolutionary ecology of the prezygotic stage. Science 303: 971–975. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

