Antihypertensive efficacy of Irbesartan/HCTZ in men and women with the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 16849900
- PMCID: PMC8109400
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2006.05486.x
Antihypertensive efficacy of Irbesartan/HCTZ in men and women with the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes
Abstract
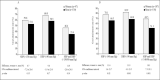
This subgroup analysis of the Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) Blood Pressure Reductions in Diverse Patient Populations (INCLUSIVE) trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of irbesartan/HCTZ fixed combinations in adults with uncontrolled systolic blood pressure (SBP) (140-159 mm Hg; 130-159 mm Hg for type 2 diabetes mellitus [T2DM]) after >or=4 weeks of antihypertensive monotherapy. Treatment was sequential: placebo (4-5 weeks), HCTZ 12.5 mg (2 weeks), irbesartan/HCTZ 150/12.5 mg (8 weeks), and irbesartan/HCTZ 300/25 mg (8 weeks). In the intent-to-treat analysis, mean change from baseline (end of placebo phase) off all previous therapy to Week 18 (study end) in T2DM patients (n=227) was -18.2+/-14.1 mm Hg for SBP (primary end point; p<0.001) and -8.7+/-8.2 mm Hg for diastolic blood pressure (p<0.001). Mean SBP/diastolic blood pressure changes in patients with the metabolic syndrome (n=345) were -21.0+/-14.3/-10.4+/-8.5 mm Hg (p<0.001). Overall, 56% (95% confidence interval, 49%-62%) of T2DM and 73% (95% confidence interval, 68%-77%) of metabolic syndrome patients achieved SBP goal (<140 mm Hg; <130 mm Hg for T2DM). Goal attainment rates were significantly higher among women with the metabolic syndrome than men. Treatments appeared to be well tolerated. Irbesartan/HCTZ fixed combinations achieved SBP goals in over half of the T2DM patients and nearly three quarters of patients with the metabolic syndrome, with SBP uncontrolled on antihypertensive monotherapy.
Figures
References
-
- Sowers JR, Haffner S. Treatment of cardiovascular and renal risk factors in the diabetic hypertensive. Hypertension. 2002;40:781–788. - PubMed
-
- Sowers JR. Treatment of hypertension in patients with diabetes. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164:1850–1857. - PubMed
-
- National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines on hypertension and antihypertensive agents in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (K/DOQI). Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43(5 suppl 1):S1–S290. - PubMed
-
- Ninomiya JK, L'ltalien G, Criqui MH, et al. Association of the metabolic syndrome with history of myocardial infarction and stroke in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Circulation. 2004;109:42–46. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association . Standards of medical care in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(suppl 1):S4–S36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical