Dopamine D1/D5 receptors gate the acquisition of novel information through hippocampal long-term potentiation and long-term depression
- PMID: 16855100
- PMCID: PMC6674280
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1454-06.2006
Dopamine D1/D5 receptors gate the acquisition of novel information through hippocampal long-term potentiation and long-term depression
Abstract
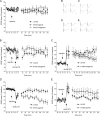
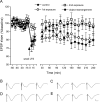
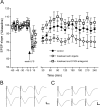
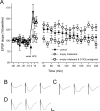
Hebbian learning models require that neurons are able to both strengthen and weaken their synaptic connections. Hippocampal synaptic plasticity, in the form of long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD), has been implicated in both spatial memory formation as well as novelty acquisition. In addition, the ventral tegmental area-hippocampal loop has been proposed to control the entry of information into long-term memory, whereas the dopaminergic system is believed to play an important role in information acquisition and synaptic plasticity. D1/D5 dopamine receptors are positively coupled to adenylyl cyclase and have been to modulate certain forms of synaptic plasticity, particularly in vitro. We investigated how D1/D5 dopamine receptors modify long-lasting synaptic plasticity at CA1 synapses of adult freely moving rats and found that receptor activation lowered the threshold for the induction of both LTP and LTD. Specific types of learning are associated with specific types of hippocampal synaptic plasticity. We found that object-configuration learning, facilitation of late-phase LTD by object exploration, and late-phase LTP by exploration of empty space were all prevented by D1/D5 receptor antagonism. Furthermore, receptor antagonism prevented electrically induced late-LTP, whereas receptor activation facilitated induction of both LTP and LTD by patterned electrical stimulation. These findings suggest that the dopaminergic system, acting via D1/D5 receptors, gates long-term changes in synaptic strength and that these changes are a critical factor in the acquisition of novel information.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antagonism of D1/D5 receptors prevents long-term depression (LTD) and learning-facilitated LTD at the perforant path-dentate gyrus synapse in freely behaving rats.Hippocampus. 2014 Dec;24(12):1615-22. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22340. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Hippocampus. 2014. PMID: 25112177
-
Synergistic requirements for the induction of dopaminergic D1/D5-receptor-mediated LTP in hippocampal slices of rat CA1 in vitro.Neuropharmacology. 2007 Jun;52(7):1547-54. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.02.010. Epub 2007 Mar 12. Neuropharmacology. 2007. PMID: 17433377
-
Frequency-dependency of the involvement of dopamine D1/D5 and beta-adrenergic receptors in hippocampal LTD triggered by locus coeruleus stimulation.Hippocampus. 2022 Jun;32(6):449-465. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23419. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Hippocampus. 2022. PMID: 35478421
-
Dopamine D1/D5 receptors mediate informational saliency that promotes persistent hippocampal long-term plasticity.Cereb Cortex. 2014 Apr;24(4):845-58. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhs362. Epub 2012 Nov 25. Cereb Cortex. 2014. PMID: 23183712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LTD, LTP, and the sliding threshold for long-term synaptic plasticity.Hippocampus. 1996;6(1):35-42. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1063(1996)6:1<35::AID-HIPO7>3.0.CO;2-6. Hippocampus. 1996. PMID: 8878740 Review.
Cited by
-
The dopamine analogue CA140 alleviates AD pathology, neuroinflammation, and rescues synaptic/cognitive functions by modulating DRD1 signaling or directly binding to Abeta.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Aug 11;21(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03180-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 39129007 Free PMC article.
-
Repetition suppression in the medial temporal lobe and midbrain is altered by event overlap.Hippocampus. 2016 Nov;26(11):1464-1477. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22622. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Hippocampus. 2016. PMID: 27479864 Free PMC article.
-
Prior Activation of 5-HT7 Receptors Modulates the Conditioned Place Preference With Methylphenidate.Front Behav Neurosci. 2019 Sep 18;13:208. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00208. eCollection 2019. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31619973 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of dopamine D1 receptor dynamics within the postsynaptic density of hippocampal glutamate synapses.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 6;8(9):e74512. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074512. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24040266 Free PMC article.
-
Linear and non-linear dose-response functions reveal a hormetic relationship between stress and learning.Dose Response. 2008 Oct 16;7(2):132-48. doi: 10.2203/dose-response.08-015.Zoladz. Dose Response. 2008. PMID: 19543480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen PH, Jansen JA (1990). Dopamine receptor agonists: selectivity and dopamine D1 receptor efficacy. Eur J Pharmacol 188:335–347. - PubMed
-
- Bear MF, Abraham WC (1996). Long-term depression in hippocampus. Annu Rev Neurosci 19:437–462. - PubMed
-
- Beckstead RM, Wooten GF, Trugman JM (1988). Distribution of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in the basal ganglia of the cat determined by quantitative autoradiography. J Comp Neurol 268:131–145. - PubMed
-
- Besheer J, Short KR, Bevins RA (2001). Dopaminergic and cholinergic antagonism in a novel-object detection task with rats. Behav Brain Res 126:211–217. - PubMed
-
- Bevins RA, Besheer J, Palmatier MI, Jensen HC, Pickett KS, Eurek S (2002). Novel-object place conditioning: behavioral and dopaminergic processes in expression of novelty reward. Behav Brain Res 129:41–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
