Dopamine D1/D5 receptors gate the acquisition of novel information through hippocampal long-term potentiation and long-term depression
- PMID: 16855100
- PMCID: PMC6674280
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1454-06.2006
Dopamine D1/D5 receptors gate the acquisition of novel information through hippocampal long-term potentiation and long-term depression
Abstract
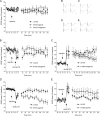
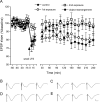
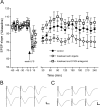
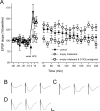
Hebbian learning models require that neurons are able to both strengthen and weaken their synaptic connections. Hippocampal synaptic plasticity, in the form of long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD), has been implicated in both spatial memory formation as well as novelty acquisition. In addition, the ventral tegmental area-hippocampal loop has been proposed to control the entry of information into long-term memory, whereas the dopaminergic system is believed to play an important role in information acquisition and synaptic plasticity. D1/D5 dopamine receptors are positively coupled to adenylyl cyclase and have been to modulate certain forms of synaptic plasticity, particularly in vitro. We investigated how D1/D5 dopamine receptors modify long-lasting synaptic plasticity at CA1 synapses of adult freely moving rats and found that receptor activation lowered the threshold for the induction of both LTP and LTD. Specific types of learning are associated with specific types of hippocampal synaptic plasticity. We found that object-configuration learning, facilitation of late-phase LTD by object exploration, and late-phase LTP by exploration of empty space were all prevented by D1/D5 receptor antagonism. Furthermore, receptor antagonism prevented electrically induced late-LTP, whereas receptor activation facilitated induction of both LTP and LTD by patterned electrical stimulation. These findings suggest that the dopaminergic system, acting via D1/D5 receptors, gates long-term changes in synaptic strength and that these changes are a critical factor in the acquisition of novel information.
Figures

References
-
- Andersen PH, Jansen JA (1990). Dopamine receptor agonists: selectivity and dopamine D1 receptor efficacy. Eur J Pharmacol 188:335–347. - PubMed
-
- Bear MF, Abraham WC (1996). Long-term depression in hippocampus. Annu Rev Neurosci 19:437–462. - PubMed
-
- Beckstead RM, Wooten GF, Trugman JM (1988). Distribution of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in the basal ganglia of the cat determined by quantitative autoradiography. J Comp Neurol 268:131–145. - PubMed
-
- Besheer J, Short KR, Bevins RA (2001). Dopaminergic and cholinergic antagonism in a novel-object detection task with rats. Behav Brain Res 126:211–217. - PubMed
-
- Bevins RA, Besheer J, Palmatier MI, Jensen HC, Pickett KS, Eurek S (2002). Novel-object place conditioning: behavioral and dopaminergic processes in expression of novelty reward. Behav Brain Res 129:41–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
