Interaction of survival and death signaling in basal forebrain neurons: roles of neurotrophins and proneurotrophins
- PMID: 16855103
- PMCID: PMC6674285
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1560-06.2006
Interaction of survival and death signaling in basal forebrain neurons: roles of neurotrophins and proneurotrophins
Abstract
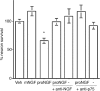
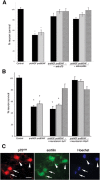
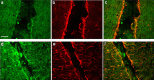
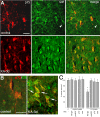
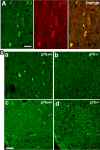
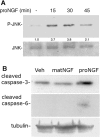
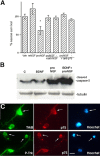
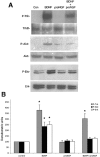
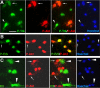
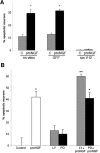
Proneurotrophins bind with high affinity to p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) and lack the capacity to bind Trk receptors, suggesting that proneurotrophins can elicit apoptosis via p75NTR even in cells expressing survival-promoting Trk receptors. In the CNS, basal forebrain (BF) neurons are particularly vulnerable to degeneration in Alzheimer's disease, and are among the few populations of brain neurons that express p75NTR throughout life. These neurons also express Trk receptors and may be concomitantly exposed to both proneurotrophins and mature neurotrophins during development, disease, or after injury. We investigated the interaction of mature and proneurotrophin signaling in these CNS neurons. Kainic acid-induced seizures elicited production of pro-NGF by BF astrocytes before caspase activation in p75NTR-positive BF neurons, demonstrating local production of proneurotrophins under pathological conditions and suggesting apoptotic signaling in vivo. Mechanisms of proneurotrophin-induced death were analyzed in cultured BF neurons, and required both p75NTR and its coreceptor sortilin. Surprisingly, exposure to both mature neurotrophins and proneurotrophins demonstrated that Trk phosphorylation did not prevent pro-NGF-induced apoptosis via p75NTR. However, activation of PI3K (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase)/Akt and MEK (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase)/Erk pathways prevented pro-NGF-induced apoptosis, revealing a novel critical checkpoint in survival versus apoptotic signaling downstream of Trk activation, and suggesting that pro-NGF blocks survival signaling by preventing Akt and Erk activation. This study shows that proneurotrophins are produced in the brain under pathological conditions, and can elicit apoptosis of BF neurons even when Trk receptors are activated.
Figures
References
-
- Alderson RF, Alterman AL, Barde Y-A, Lindsay RM (1990). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor increases survival and differentiated functions of rat septal cholinergic neurons in culture. Neuron 5:297–306. - PubMed
-
- Barker PA (2004). p75NTR is positively promiscuous: novel partners and new insights. Neuron 42:529–533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
