DNA supercoiling and the Lrp protein determine the directionality of fim switch DNA inversion in Escherichia coli K-12
- PMID: 16855224
- PMCID: PMC1540041
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00344-06
DNA supercoiling and the Lrp protein determine the directionality of fim switch DNA inversion in Escherichia coli K-12
Abstract
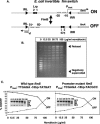
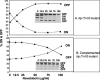
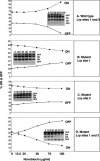
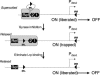
Site-specific recombinases of the integrase family usually require cofactors to impart directionality in the recombination reactions that they catalyze. The FimB integrase inverts the Escherichia coli fim switch (fimS) in the on-to-off and off-to-on directions with approximately equal efficiency. Inhibiting DNA gyrase with novobiocin caused inversion to become biased in the off-to-on direction. This directionality was not due to differential DNA topological distortion of fimS in the on and off phases by the activity of its resident P(fimA) promoter. Instead, the leucine-responsive regulatory (Lrp) protein was found to determine switching outcomes. Knocking out the lrp gene or abolishing Lrp binding sites 1 and 2 within fimS completely reversed the response of the switch to DNA relaxation. Inactivation of either Lrp site alone resulted in mild on-to-off bias, showing that they act together to influence the response of the switch to changes in DNA supercoiling. Thus, Lrp is not merely an architectural element organizing the fim invertasome, it collaborates with DNA supercoiling to determine the directionality of the DNA inversion event.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DNA relaxation-dependent phase biasing of the fim genetic switch in Escherichia coli depends on the interplay of H-NS, IHF and LRP.Mol Microbiol. 2009 Dec;74(5):1071-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06919.x. Epub 2009 Nov 2. Mol Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19889099
-
DNA sequence heterogeneity in Fim tyrosine-integrase recombinase-binding elements and functional motif asymmetries determine the directionality of the fim genetic switch in Escherichia coli K-12.Mol Microbiol. 2008 Jan;67(1):171-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.06037.x. Epub 2007 Nov 20. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18034794
-
The leucine-responsive regulatory protein binds to the fim switch to control phase variation of type 1 fimbrial expression in Escherichia coli K-12.J Bacteriol. 1994 Sep;176(18):5665-72. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.18.5665-5672.1994. J Bacteriol. 1994. PMID: 7916011 Free PMC article.
-
The intricate workings of a bacterial epigenetic switch.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2004;547:83-9. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-8861-4_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2004. PMID: 15230094 Review.
-
Bacterial DNA topology and infectious disease.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Feb;37(3):672-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn996. Epub 2008 Dec 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19073701 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Type 1 fimbriae, a colonization factor of uropathogenic Escherichia coli, are controlled by the metabolic sensor CRP-cAMP.PLoS Pathog. 2009 Feb;5(2):e1000303. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000303. Epub 2009 Feb 20. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19229313 Free PMC article.
-
Two-component system GrpP/GrpQ promotes pathogenicity of uropathogenic Escherichia coli CFT073 by upregulating type 1 fimbria.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 11;16(1):607. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-55982-z. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39799152 Free PMC article.
-
yqhG Contributes to Oxidative Stress Resistance and Virulence of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli and Identification of Other Genes Altering Expression of Type 1 Fimbriae.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Aug 29;9:312. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00312. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31555608 Free PMC article.
-
The leucine-responsive regulatory protein, Lrp, activates transcription of the fim operon in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium via the fimZ regulatory gene.J Bacteriol. 2008 Jan;190(2):602-12. doi: 10.1128/JB.01388-07. Epub 2007 Nov 2. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 17981960 Free PMC article.
-
Phase variation of Clostridium difficile virulence factors.Gut Microbes. 2018 Jan 2;9(1):76-83. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2017.1362526. Epub 2017 Sep 21. Gut Microbes. 2018. PMID: 28806147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benjamin, K. R., A. P. Abola, R. Kanaar, and N. R. Cozzarelli. 1996. Contributions of supercoiling to Tn3 resolvase and phage Mu Gin site-specific recombination. J. Mol. Biol. 256:50-65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

