Multilocus sequence typing as an approach for population analysis of Medicago-nodulating rhizobia
- PMID: 16855247
- PMCID: PMC1540022
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00335-06
Multilocus sequence typing as an approach for population analysis of Medicago-nodulating rhizobia
Abstract
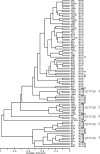
Multilocus sequence typing (MLST), a sequence-based method to characterize bacterial genomes, was used to examine the genetic structure in a large collection of Medicago-nodulating rhizobial strains. This is the first study where MLST has been applied in conjunction with eBURST analysis to determine the population genetic structure of nonpathogenic bacteria recovered from the soil environment. Sequence variation was determined in 10 chromosomal loci of 231 strains that predominantly originated from southwest Asia. Genetic diversity for each locus ranged from 0.351 to 0.819, and the strains examined were allocated to 91 different allelic profiles or sequence types (STs). The genus Medicago is nodulated by at least two groups of rhizobia with divergent chromosomes that have been classified as Sinorhizobium meliloti and Sinorhizobium medicae. Evidence was obtained that the degree of genetic exchange among the chromosomes across these groups is limited. The symbiosis with Medicago polymorpha of nine strains placed in one of these groups, previously identified as S. medicae, ranged from ineffective to fully effective, indicating that there was no strong relationship between symbiotic phenotype and chromosomal genotype.
Figures

References
-
- Badri, Y., K. Zribi, M. Badri, T. Huguet, and M. E. Aouani. 2003. Sinorhizobium meliloti nodulates Medicago laciniata in Tunisian soils. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 39(Special Issue):178-183.
-
- Biondi, E. G., E. Pilli, E. Giuntini, M. L. Roumiantseva, E. E. Andronov, O. P. Onichtchouk, O. N. Kurchak, B. V. Simarov, N. I. Dzyubenko, A. Mengoni, and M. Bazzicalupo. 2003. Genetic relationship of Sinorhizobium meliloti and Sinorhizobium medicae strains isolated from Caucasian region. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 220:207-213. - PubMed
-
- Bradić, M., S. Sikora, S. Redžepović, and Z. Štafa. 2003. Genetic identification and symbiotic efficiency of an indigenous Sinorhizobium meliloti field population. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 41:69-75.
-
- Capela, D., F. Barloy-Hubler, J. Gouzy, G. Bothe, F. Ampe, J. Batut, P. Boistard, A. Becker, M. Boutry, E. Cadieu, S. Dreano, S. Gloux, T. Godrie, A. Goffeau, D. Kahn, E. Kiss, V. Lelaure, D. Masuy, T. Pohl, D. Portetelle, A. Pühler, B. Purnelle, U. Ramsperger, C. Renard, P. Thebault, M. Vandenbol, S. Weidner, and F. Galibert. 2001. Analysis of the chromosome sequence of the legume symbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti strain 1021. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:9877-9882. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

