The WD40-repeat protein Pwp1p associates in vivo with 25S ribosomal chromatin in a histone H4 tail-dependent manner
- PMID: 16855292
- PMCID: PMC1524916
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl487
The WD40-repeat protein Pwp1p associates in vivo with 25S ribosomal chromatin in a histone H4 tail-dependent manner
Abstract
The tails of core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) are critical for the regulation of chromatin dynamics. Each core histone tail is specifically recognized by various tail binding proteins. Here we screened for budding yeast histone H4-tail binding proteins in a protein differential display approach by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2DGE). To obtain highly enriched chromatin proteins, we used a Mg2+-dependent chromatin oligomerization technique. The Mg2+-dependent oligomerized chromatin from H4-tail deleted cells was compared with that from wild-type cells. We used mass spectrometry to identify 22 candidate proteins whose amounts were reduced in the oligomerized chromatin from the H4-tail deleted cells. A Saccharomyces Genome Database search revealed 10 protein complexes, each of which contained more than two candidate proteins. Interestingly, 7 out of the 10 complexes have the potential to associate with the H4-tail. We obtained in vivo evidence, by a chromatin immunoprecipitation assay, that one of the candidate proteins, Pwp1p, associates with the 25S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) chromatin in an H4-tail-dependent manner. We propose that the complex containing Pwp1p regulates the transcription of rDNA. Our results demonstrate that the protein differential display approach by 2DGE, using a histone-tail mutant, is a powerful method to identify histone-tail binding proteins.
Figures

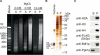


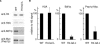

References
-
- Luger K., Mader A.W., Richmond R.K., Sargent D.F., Richmond T.J. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 Å resolution. Nature. 1997;389:251–260. - PubMed
-
- Hansen J.C. Conformational dynamics of the chromatin fiber in solution: determinants, mechanisms, and functions. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2002;31:361–392. - PubMed
-
- Zheng C., Lu X, Hansen J.C., Hayes J.J. Salt-dependent intra- and internucleosomal interactions of the H3 tail domain in a model oligonucleosomal array. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:33552–33557. - PubMed
-
- Hecht A., Laroche T., Strahl-Bolsinger S., Gasser S.M., Grunstein M. Histone H3 and H4 N-termini interact with SIR3 and SIR4 proteins: a molecular model for the formation of heterochromatin in yeast. Cell. 1995;80:583–592. - PubMed
-
- Carmen A.A., Milne L., Grunstein M. Acetylation of the yeast histone H4 N terminus regulates its binding to heterochromatin protein SIR3. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:4778–4781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

