Genome-wide linkage analysis of heroin dependence in Han Chinese: results from wave one of a multi-stage study
- PMID: 16856125
- PMCID: PMC2562776
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30361
Genome-wide linkage analysis of heroin dependence in Han Chinese: results from wave one of a multi-stage study
Abstract
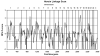
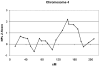
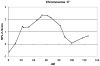
The contribution of genes to the etiology of heroin dependence is greater than for any other illicit drug. The specific genes mediating this effect remain unknown, despite several candidate gene association studies of the condition. Here we report the results of a genome-wide search for heroin dependence susceptibility loci using multipoint linkage analysis. In phase I, we ascertained 207 independent affected sibling pairs from 202 Han Chinese families from Yunnan Province, China (near Asia's "Golden Triangle"). After data-cleaning, 194 fully independent sibling pairs (i.e., with no overlapping individuals) from 192 families were genotyped on 404 short tandem-repeat markers spaced at an average inter-marker distance of 9 cM. Although none of our findings achieved genome-wide significance, we found two regions with non-parametric linkage (NPL) Z-scores greater than 2.0. An NPL Z-score of 2.19 (uncorrected P-value = 0.014) was observed at D4S1644, located at 143.3 cM on chromosomal region 4q31.21. The highest NPL Z-score of 2.36 (uncorrected P-value = 0.009) was observed at 53.4 cM on chromosomal region 17q11.2 at marker D17S1880. This is among the first published reports of a genome-wide linkage analysis of heroin dependence. Forthcoming results from other groups and from two additional waves of ascertainment (one planned, one currently ongoing) for our own study should be able to support or refute the putative susceptibility loci we have identified, after which positional candidate genes can be further evaluated as risk factors for the illness.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide linkage analysis of heroin dependence in Han Chinese: results from Wave Two of a multi-stage study.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2008 Nov 1;98(1-2):30-4. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2008.04.011. Epub 2008 Jun 6. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2008. PMID: 18538955 Free PMC article.
-
Linkage of hypertension to chromosome 2q14-q23 in Chinese families.J Hypertens. 2001 Jan;19(1):55-61. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200101000-00008. J Hypertens. 2001. PMID: 11204305
-
Evidence for a major psoriasis susceptibility locus at 6p21(PSORS1) and a novel candidate region at 4q31 by genome-wide scan in Chinese hans.J Invest Dermatol. 2002 Dec;119(6):1361-6. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2002.19612.x. J Invest Dermatol. 2002. PMID: 12485440
-
Two-dimensional genome scan identifies multiple genetic interactions in bipolar affective disorder.Biol Psychiatry. 2010 Mar 1;67(5):478-86. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.10.022. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Biol Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20022591 Review.
-
The genetics of autism.Pediatrics. 2004 May;113(5):e472-86. doi: 10.1542/peds.113.5.e472. Pediatrics. 2004. PMID: 15121991 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of OPRM1 variants in heroin dependence by family-based association testing and meta-analysis.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2007 Oct 8;90(2-3):159-65. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2007.02.022. Epub 2007 Apr 9. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2007. PMID: 17416470 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide linkage analysis of heroin dependence in Han Chinese: results from Wave Two of a multi-stage study.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2008 Nov 1;98(1-2):30-4. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2008.04.011. Epub 2008 Jun 6. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2008. PMID: 18538955 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study identifies genes that may contribute to risk for developing heroin addiction.Psychiatr Genet. 2010 Oct;20(5):207-14. doi: 10.1097/YPG.0b013e32833a2106. Psychiatr Genet. 2010. PMID: 20520587 Free PMC article.
-
Association between serotonin transporter gene polymorphisms and heroin dependence: a meta-analytic study.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016 Nov 30;12:3061-3067. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S120786. eCollection 2016. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016. PMID: 27942217 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype patterns that contribute to increased risk for or protection from developing heroin addiction.Mol Psychiatry. 2008 Apr;13(4):417-28. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4002147. Epub 2008 Jan 15. Mol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18195715 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abecasis GR, Cherny SS, Cookson WO, Cardon LR. GRR: graphical representation of relationship errors. Bioinformatics. 2001;17(8):742–3. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-IV) Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- Beyrer C, Razak MH, Lisam K, Chen J, Lui W, Yu XF. Overland heroin trafficking routes and HIV-1 spread in south and south-east Asia. Aids. 2000;14(1):75–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

