Synaptic input to OFF parasol ganglion cells in macaque retina
- PMID: 16856174
- PMCID: PMC3128437
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.21040
Synaptic input to OFF parasol ganglion cells in macaque retina
Abstract
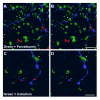
A Neurobiotin-injected OFF parasol cell from midperipheral macaque retina was studied by reconstruction of serial ultrathin sections and compared with ON parasol cells studied previously. In most respects, the synaptic inputs to the two subtypes were similar. Only a few of the amacrine cell processes that provided input to the labeled OFF parasol ganglion cell dendrites made or received inputs within the series, and none of these interactions were with the bipolar cells or other amacrine cells presynaptic to the OFF parasol cell. These findings suggest that the direct inhibitory input to OFF parasol cells originates from other areas of the retina. OFF parasol cells were known to receive inputs from two types of diffuse bipolar cells. To identify candidates for the presynaptic amacrine cells, OFF parasol cells were labeled with Lucifer yellow by using a juxtacellular labeling technique, and amacrine cells known to costratify with them were labeled via immunofluorescent methods. Appositions were observed with amacrine cells containing immunoreactive calretinin, parvalbumin, choline acetylatransferase, and G6-Gly, a cholecystokinin precursor. These findings suggest that the inhibitory input to parasol cells conveys information about several different attributes of visual stimuli and, particularly, about their global properties.
Figures







References
-
- Boycott BB, Wässle H. Morphological classification of bipolar cells of the primate retina. Eur J Neurosci. 1991;3:1069–1088. - PubMed
-
- Burr DC, Morrone MC, Ross J. Selective suppression of the magnocellular visual pathway during saccadic eye movements. Nature. 1994;371:511–3. - PubMed
-
- Calkins DJ. Synaptic orgainization of cone pathways in the primate retina. In: Gegenfurtner KR, Sharpe LT, editors. Color Vision: From Genes to Perception. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 1999. pp. 163–179.
-
- Calkins DJ, Schein SJ, Tsukamoto Y, Sterling P. M and L cones in macaque fovea connect to midget ganglion cells by different numbers of excitatory synapses. Nature. 1994;371:70–72. - PubMed
-
- Calkins DJ, Sterling P. Absence of spectrally specific lateral inputs to midget ganglion cells in primate retina. Nature. 1996;381:613–615. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

