Pulling on the nascent RNA during transcription does not alter kinetics of elongation or ubiquitous pausing
- PMID: 16857589
- PMCID: PMC1513632
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.06.023
Pulling on the nascent RNA during transcription does not alter kinetics of elongation or ubiquitous pausing
Abstract
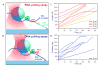
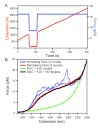
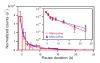
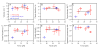
Transcriptional elongation and termination by RNA polymerase (RNAP) are controlled by interactions among the nascent RNA, DNA, and RNAP that comprise the ternary transcription elongation complex (TEC). To probe the effects of cotranscriptionally folded RNA hairpins on elongation as well as the stability of the TEC, we developed a single-molecule assay to monitor RNA elongation by Escherichia coli RNAP molecules while applying controlled loads to the nascent RNA that favor forward translocation. Remarkably, forces up to 30 pN, twice those required to disrupt RNA secondary structure, did not significantly affect enzyme processivity, transcription elongation rates, pause frequencies, or pause lifetimes. These results indicate that ubiquitous transcriptional pausing is not a consequence of the formation of hairpins in the nascent RNA. The ability of the TEC to sustain large loads on the transcript reflects a tight binding of RNA within the TEC and has important implications for models of transcriptional termination.
Figures
References
-
- Adelman K, Yuzenkova J, La Porta A, Zenkin N, Lee J, Lis JT, Borukhov S, Wang MD, Severinov K. Molecular mechanism of transcription inhibition by Peptide antibiotic microcin j25. Mol Cell. 2004;14:753–762. - PubMed
-
- Artsimovitch I, Landick R. The transcriptional regulator RfaH stimulates RNA chain synthesis after recruitment to elongation complexes by the exposed nontemplate DNA strand. Cell. 2002;109:193–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

