Nitric oxide inhibits exocytosis of cytolytic granules from lymphokine-activated killer cells
- PMID: 16857739
- PMCID: PMC1544231
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0600275103
Nitric oxide inhibits exocytosis of cytolytic granules from lymphokine-activated killer cells
Abstract
NO inhibits cytotoxic T lymphocyte killing of target cells, although the precise mechanism is unknown. We hypothesized that NO decreases exocytosis of cytotoxic granules from activated lymphocytes. We now show that NO inhibits lymphokine-activated killer cell killing of K562 target cells. Exogenous and endogenous NO decreases the release of granzyme B, granzyme A, and perforin: all contents of cytotoxic granules. NO inhibits the signal transduction cascade initiated by cross-linking of the T cell receptor that leads to granule exocytosis. In particular, we found that NO decreases the expression of Ras, a critical signaling component within the exocytic pathway. Ectopic expression of Ras prevents NO inhibition of exocytosis. Our data suggest that Ras mediates NO inhibition of lymphocyte cytotoxicity and emphasize that alterations in the cellular redox state may regulate the exocytic signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
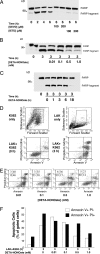


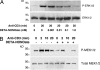


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL56091/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL70929/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL065608/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL056091/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL72518/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL65608/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL63706/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL072518/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HL070929/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL074061/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL063706/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070929/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

