Gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor interaction with Smad3 inhibits myofibroblast differentiation
- PMID: 16858008
- PMCID: PMC1899300
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0043OC
Gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor interaction with Smad3 inhibits myofibroblast differentiation
Abstract
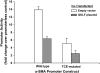
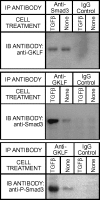
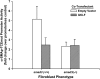
Gut-enriched Krüppel-like factor (GKLF) has been reported to partially inhibit alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA) gene transcription by competing for binding to the TGF-beta control element (TCE) with known activators such as Sp1 and other Krüppel-like factors. This incomplete inhibition via the TCE suggests an additional mechanism, which was evaluated in this study. The results showed that an alpha-SMA promoter mutated in the TCE remained susceptible to inhibition by GKLF in rat lung fibroblasts consistent with the existence of an additional TCE-independent mechanism. Since TGF-beta- induced alpha-SMA expression is Smad3-dependent, potential interaction between GKLF and Smad3 was examined as a basis for this additional inhibitory mechanism. Co-immunoprecipitation and yeast two-hybrid assays revealed that GKLF could bind Smad3 through the Smad3 MH2 domain. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays and ChIP assay indicated that this GKLF-Smad3 interaction inhibited Smad3 binding to the Smad3-binding element (SBE) in the alpha-SMA promoter, and the activity of an SBE containing artificial promoter. Further analysis using smad3(-/-) fibroblasts confirmed that the TCE-independent inhibition by GKLF was dependent on Smad3. These data taken together suggest that in addition to inhibition via the TCE, GKLF represses alpha-SMA gene expression by interacting with Smad3 to prevent Smad3 binding to the SBE. It represents the first evidence to directly link GKLF with Smad3, a key intracellular mediator of TGF-beta signaling, which should lead to a clearer understanding of the mechanism of how GKLF regulates TGF-beta-induced gene expression.
Figures



References
-
- Pardo A, Selman M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: new insights in its pathogenesis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2002;34:1534–1538. - PubMed
-
- Campbell JH, Kocher O, Skalli O, Gabbiani G, Campbell GR. Cytodifferentiation and expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin mRNA and protein during primary culture of aortic smooth muscle cells: correlation with cell density and proliferative state. Arteriosclerosis 1989;9: 633–643. - PubMed
-
- Woodcock-Mitchell J, Mitchell JJ, Low RB, Kieny M, Sengel P, Rubbia L, Skalli O, Jackson B, Gabbiani G. Alpha-smooth muscle actin is transiently expressed in embryonic rat cardiac and skeletal muscles. Differentiation 1988;39:161–166. - PubMed
-
- Hu B, Wu Z, Phan SH. Smad3 mediates transforming growth factor-β–induced alpha-smooth muscle actin expression. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2003;29:397–404. - PubMed
-
- Darby I, Skalli O, Gabbiani G. Alpha-smooth muscle actin is transiently expressed by myofibroblasts during experimental wound healing. Lab Invest 1990;63:21–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

