One hundred two consecutive hepatobiliary resections for perihilar cholangiocarcinoma with zero mortality
- PMID: 16858186
- PMCID: PMC1602147
- DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000217605.66519.38
One hundred two consecutive hepatobiliary resections for perihilar cholangiocarcinoma with zero mortality
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the short-term surgical outcome of hepatobiliary resections for perihilar cholangiocarcinoma in the last 5 years.
Summary background data: Hepatobiliary resection for perihilar cholangiocarcinoma remains a technically demanding procedure, calling for a high level of expertise in biliary and hepatic surgery, and is still associated with significant morbidity or mortality.
Methods: Between 2000 and 2004, we surgically treated 102 consecutive patients with perihilar cholangiocarcinoma with a management strategy consisting of preoperative biliary drainage, portal vein embolization (for right-sided and extended left-sided resections), and major hepatobiliary resection. The data on all of the patients were analyzed retrospectively to identify the factors that might significantly affect the postoperative mortality and morbidity.
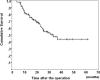
Results: There were no cases of in-hospital mortality or postoperative liver failure. Major complications were encountered in 7 patients (6.9%), and the overall morbidity rate was 50%. Reoperation was required in 2 patients (2%). The overall median length of postoperative hospital stay was 26 days (range, 13-119 days). Univariate analysis in relation to the postoperative morbidity showed significant differences in the preoperative occurrence of segmental cholangitis or cholecystitis (P = 0.015), the severity of postoperative hyperbilirubinemia (P < 0.001), and the total amount of fresh frozen plasma administered (P = 0.002). Multivariate analysis revealed a single independent significant predictive factor for postoperative morbidity, namely, preoperative cholangitis or cholecystitis (odds ratio, 9.08; 95% confidence interval, 1.05-78.56, P = 0.045).
Conclusions: Our experience indicates that hepatobiliary resections for perihilar cholangiocarcinoma can be conducted safely, without a single case of postoperative liver failure or mortality. Occurrence of preoperative cholangitis or cholecystitis is a significant indicator for morbidity of major hepatobiliary resection.
Figures
References
-
- Nimura Y, Hayakawa N, Kamiya J, et al. Hepatic segmentectomy with caudate lobe resection for bile duct carcinoma of the hepatic hilus. World J Surg. 1990;14:535–543. - PubMed
-
- Nimura Y, Hayakawa N, Kamiya J, et al. Hepatopancreatoduodenectomy for advanced carcinoma of the biliary tract. Hepatogastroenterology. 1991;38:170–175. - PubMed
-
- Klempnauer J, Ridder GJ, von Wasielewski R, et al. Resectional surgery of hilar cholangiocarcinoma: a multivariate analysis of prognostic factors. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:947–954. - PubMed
-
- Nimura Y, Kamiya J, Kondo S, et al. Aggressive preoperative management and extended surgery for hilar cholangiocarcinoma: Nagoya experience. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2000;7:155–62. - PubMed
-
- Lee SG, Lee YJ, Park KM, et al. One hundred and eleven liver resections for hilar bile duct cancer. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2000;7:135–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

