Acetylation and MAPK phosphorylation cooperate to regulate the degradation of active GATA-1
- PMID: 16858405
- PMCID: PMC1523174
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601228
Acetylation and MAPK phosphorylation cooperate to regulate the degradation of active GATA-1
Abstract
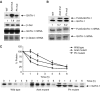
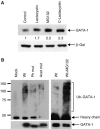
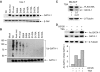
Regulation of transcription requires mechanisms to both activate and terminate transcription factor activity. GATA-1 is a key haemopoietic transcription factor whose activity is increased by acetylation. We show here that acetylated GATA-1 is targeted for degradation via the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway. Acetylation positively signals ubiquitination, suggesting that activation by acetylation simultaneously marks GATA-1 for degradation. Promoter-specific MAPK phosphorylation then cooperates with acetylation to execute protein loss. The requirement for both modifications is novel and suggests a way by which degradation of the active protein can be specifically regulated in response to external phosphorylation-mediated signalling. As many transcription factors are activated by acetylation, we suggest that this might be a general mechanism to control transcription factor activity.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase in the cytokine-regulated phosphorylation of transcription factor GATA-1.Hematol J. 2004;5(3):262-72. doi: 10.1038/sj.thj.6200345. Hematol J. 2004. PMID: 15167914
-
HSP27 controls GATA-1 protein level during erythroid cell differentiation.Blood. 2010 Jul 8;116(1):85-96. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-241778. Epub 2010 Apr 21. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20410505
-
Acetylation of GATA-1 is required for chromatin occupancy.Blood. 2006 Dec 1;108(12):3736-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-032847. Epub 2006 Aug 3. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16888089 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of RUNX1 transcriptional function by GATA-1.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2007;17(4):271-80. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v17.i4.20. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2007. PMID: 17725493 Review.
-
TNFR signaling: ubiquitin-conjugated TRAFfic signals control stop-and-go for MAPK signaling complexes.Immunol Rev. 2009 Mar;228(1):225-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00755.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19290931 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein kinase D-HDAC5 signaling regulates erythropoiesis and contributes to erythropoietin cross-talk with GATA1.Blood. 2012 Nov 15;120(20):4219-28. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-10-387050. Epub 2012 Sep 14. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22983445 Free PMC article.
-
IKK phosphorylates Huntingtin and targets it for degradation by the proteasome and lysosome.J Cell Biol. 2009 Dec 28;187(7):1083-99. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200909067. Epub 2009 Dec 21. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 20026656 Free PMC article.
-
Compounds targeting class II histone deacetylases do not cause panHDACI-associated impairment of megakaryocyte differentiation.Exp Hematol. 2019 Apr;72:36-46. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2018.12.007. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Exp Hematol. 2019. PMID: 30611870 Free PMC article.
-
Linking post-translational modifications and protein turnover by site-resolved protein turnover profiling.Nat Commun. 2022 Jan 10;13(1):165. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27639-0. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35013197 Free PMC article.
-
A study of bias and increasing organismal complexity from their post-translational modifications and reaction site interplays.Brief Bioinform. 2017 Jan;18(1):69-84. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbv111. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Brief Bioinform. 2017. PMID: 26764274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyes J, Byfield P, Nakatani Y, Ogryzko V (1998) Regulation of activity of the transcription factor GATA-1 by acetylation. Nature 396: 594–598 - PubMed
-
- Cairns L, Ciro M, Minuzzo M, Morle F, Starck J, Ottolenghi S, Ronchi A (2003) Induction of globin mRNA expression by interleukin-3 in a stem cell factor-dependent SV-40 T-antigen-immortalized multipotent hematopoietic cell line. J Cell Physiol 195: 38–49 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

