Modulation of face-sensitive event-related potentials by canonical and distorted human faces: the role of vertical symmetry and up-down featural arrangement
- PMID: 16859419
- PMCID: PMC3063065
- DOI: 10.1162/jocn.2006.18.8.1343
Modulation of face-sensitive event-related potentials by canonical and distorted human faces: the role of vertical symmetry and up-down featural arrangement
Abstract
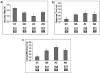
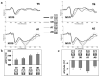
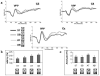
This study examined the sensitivity of early face-sensitive event-related potential (ERP) components to the disruption of two structural properties embedded in faces, namely, "updown featural arrangement" and "vertical symmetry." Behavioral measures and ERPs were recorded as adults made an orientation judgment for canonical faces and distorted faces that had been manipulated for either or both of the mentioned properties. The P1, the N170, and the vertex positive potential (VPP) exhibited a similar gradient in sensitivity to the two investigated properties, in that they all showed a linear increase in amplitude or latency as the properties were selectively disrupted in the order of (1) up-down featural arrangement, (2) vertical symmetry, and (3) both up-down featural arrangement and vertical symmetry. Exceptions to this finding were seen for the amplitudes of the N170 and VPP, which were largest for the stimulus in which solely vertical symmetry was disrupted. Interestingly, the enhanced amplitudes of the N170 and VPP are consistent with a drop in behavioral performance on the orientation judgment for this stimulus.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interplay between familiarity and orientation in face processing: an ERP study.Int J Psychophysiol. 2007 Sep;65(3):182-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2007.04.003. Epub 2007 Apr 13. Int J Psychophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17512996
-
Stepwise emergence of the face-sensitive N170 event-related potential component.Neuroreport. 2003 Nov 14;14(16):2035-9. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200311140-00006. Neuroreport. 2003. PMID: 14600493
-
Developmental and individual differences on the P1 and N170 ERP components in children with and without autism.Dev Neuropsychol. 2011;36(2):214-36. doi: 10.1080/87565641.2010.549870. Dev Neuropsychol. 2011. PMID: 21347922 Free PMC article.
-
Early holistic face-like processing of Arcimboldo paintings in the right occipito-temporal cortex: evidence from the N170 ERP component.Int J Psychophysiol. 2013 Nov;90(2):157-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2013.06.024. Epub 2013 Jun 29. Int J Psychophysiol. 2013. PMID: 23816562
-
The effect of scrambling upright and inverted faces on the N170.Q J Exp Psychol (Hove). 2018 Nov;71(11):2464-2476. doi: 10.1177/1747021817744455. Epub 2018 Jan 1. Q J Exp Psychol (Hove). 2018. PMID: 30362407
Cited by
-
Impact of total sleep deprivation on behavioural neural processing of emotionally expressive faces.Exp Brain Res. 2014 May;232(5):1429-42. doi: 10.1007/s00221-013-3780-1. Epub 2013 Dec 8. Exp Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24317639
-
Face distortion aftereffects evoked by featureless first-order stimulus configurations.Front Psychol. 2012 Dec 17;3:566. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00566. eCollection 2012. Front Psychol. 2012. PMID: 23403400 Free PMC article.
-
The neural correlates of processing newborn and adult faces in 3-year-old children.Dev Sci. 2013 Nov;16(6):905-14. doi: 10.1111/desc.12063. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Dev Sci. 2013. PMID: 24118716 Free PMC article.
-
Spatio-temporal dynamics and laterality effects of face inversion, feature presence and configuration, and face outline.Front Hum Neurosci. 2014 Nov 10;8:868. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00868. eCollection 2014. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25426044 Free PMC article.
-
Use of event-related potentials in the study of typical and atypical development.J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2008 Nov;47(11):1252-61. doi: 10.1097/CHI.0b013e318185a6d8. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18827722 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akhtar N, Enns JT. Relations between covert orienting and filtering in the development of visual attention. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology. 1989;48:315–334. - PubMed
-
- Bentin S, Deouell LY. Structural encoding and identification in face processing: ERP evidence for separate mechanisms. Cognitive Neuropsychology. 2000;17:35–54. - PubMed
-
- Botzel K, Schulze S, Stodieck SR. Scalp topography and analysis of intracranial sources of face-evoked potentials. Experimental Brain Research. 1995;104:135–143. - PubMed
-
- Bruce V, Young A. Understanding face recognition. British Journal of Psychology. 1986;77:305–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

