A protein extension to shorten RNA: elongated elongation factor-Tu recognizes the D-arm of T-armless tRNAs in nematode mitochondria
- PMID: 16859488
- PMCID: PMC1609916
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20060781
A protein extension to shorten RNA: elongated elongation factor-Tu recognizes the D-arm of T-armless tRNAs in nematode mitochondria
Abstract
Nematode mitochondria possess extremely truncated tRNAs. Of 22 tRNAs, 20 lack the entire T-arm. The T-arm is necessary for the binding of canonical tRNAs and EF (elongation factor)-Tu (thermo-unstable). The nematode mitochondrial translation system employs two different EF-Tu factors named EF-Tu1 and EF-Tu2. Our previous study showed that nematode Caenorhabditis elegans EF-Tu1 binds specifically to T-armless tRNA. C. elegans EF-Tu1 has a 57-amino acid C-terminal extension that is absent from canonical EF-Tu, and the T-arm-binding residues of canonical EF-Tu are not conserved. In this study, the recognition mechanism of T-armless tRNA by EF-Tu1 was investigated. Both modification interference assays and primer extension analysis of cross-linked ternary complexes revealed that EF-Tu1 interacts not only with the tRNA acceptor stem but also with the D-arm. This is the first example of an EF-Tu recognizing the D-arm of a tRNA. The binding activity of EF-Tu1 was impaired by deletion of only 14 residues from the C-terminus, indicating that the C-terminus of EF-Tu1 is required for its binding to T-armless tRNA. These results suggest that C. elegans EF-Tu1 recognizes the D-arm instead of the T-arm by a mechanism involving its C-terminal region. This study sheds light on the co-evolution of RNA and RNA-binding proteins in nematode mitochondria.
Figures

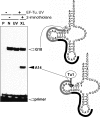
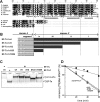
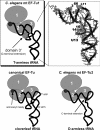
Comment in
-
Intricacies and surprises of nuclear-mitochondrial co-evolution.Biochem J. 2006 Oct 15;399(2):e7-9. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061241. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16987107 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sprinzl M. Elongation factor Tu: a regulatory GTPase with an integrated effector. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1994;19:245–250. - PubMed
-
- Nissen P., Kjeldgaard M., Thirup S., Polekhina G., Reshetnikova L., Clark B. F., Nyborg J. Crystal structure of the ternary complex of Phe-tRNAPhe, EF-Tu, and a GTP analog. Science. 1995;270:1464–1472. - PubMed
-
- Nissen P., Thirup S., Kjeldgaard M., Nyborg J. The crystal structure of Cys-tRNACys-EF-Tu-GDPNP reveals general and specific features in the ternary complex and in tRNA. Structure. 1999;7:143–156. - PubMed
-
- Clark B. F. C., Kjeldgaard M., Barciszewski J., Sprinzl M. Recognition of aminoacyl-tRNAs by protein elongation factors. tRNA: Structure, Biosynthesis, and Function. In: Soll D., RajBhandary U. L., editors. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology; 1995. pp. 423–442.
-
- Rudinger J., Blechschmidt B., Ribeiro S., Sprinzl M. Minimalist aminoacylated RNAs as efficient substrates for elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1994;33:5682–5688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

