Beta3 integrin and Src facilitate transforming growth factor-beta mediated induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 16859511
- PMCID: PMC1779461
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr1524
Beta3 integrin and Src facilitate transforming growth factor-beta mediated induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
Introduction: Transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta suppresses breast cancer formation by preventing cell cycle progression in mammary epithelial cells (MECs). During the course of mammary tumorigenesis, genetic and epigenetic changes negate the cytostatic actions of TGF-beta, thus enabling TGF-beta to promote the acquisition and development of metastatic phenotypes. The molecular mechanisms underlying this conversion of TGF-beta function remain poorly understood but may involve signaling inputs from integrins.
Methods: beta3 Integrin expression or function in MECs was manipulated by retroviral transduction of active or inactive beta3 integrins, or by transient transfection of small interfering RNA (siRNA) against beta3 integrin. Altered proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) stimulated by TGF-beta in control and beta3 integrin manipulated MECs was determined. Src involvement in beta3 integrin mediated alterations in TGF-beta signaling was assessed by performing Src protein kinase assays, and by interdicting Src function pharmacologically and genetically.
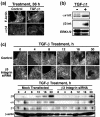
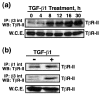
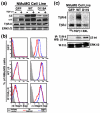
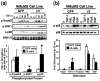
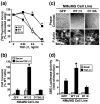
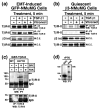
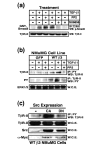
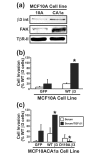
Results: TGF-beta stimulation induced alphavbeta3 integrin expression in a manner that coincided with EMT in MECs. Introduction of siRNA against beta3 integrin blocked its induction by TGF-beta and prevented TGF-beta stimulation of EMT in MECs. beta3 integrin interacted physically with the TGF-beta receptor (TbetaR) type II, thereby enhancing TGF-beta stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), and of Smad2/3-mediated gene transcription in MECs. Formation of beta3 integrin:TbetaR-II complexes blocked TGF-beta mediated growth arrest and increased TGF-beta mediated invasion and EMT. Dual beta3 integrin:TbetaR-II activation induced tyrosine phosphorylation of TbetaR-II, a phosphotransferase reaction mediated by Src in vitro. Inhibiting Src activity in MECs prevented the ability of beta3 integrin to induce TbetaR-II tyrosine phosphorylation, MAPK activation, and EMT stimulated by TGF-beta. Lastly, wild-type and D119A beta3 integrin expression enhanced and abolished, respectively, TGF-beta stimulation of invasion in human breast cancer cells.
Conclusion: We show that beta3 integrin alters TGF-beta signaling in MECs via Src-mediated TbetaR-II tyrosine phosphorylation, which significantly enhanced the ability of TGF-beta to induce EMT and invasion. Our findings suggest that beta3 integrin interdiction strategies may represent an innovative approach to re-establishing TGF-beta mediated tumor suppression in progressing human breast cancers.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Therapeutic targeting of the focal adhesion complex prevents oncogenic TGF-beta signaling and metastasis.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(5):R68. doi: 10.1186/bcr2360. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19740433 Free PMC article.
-
Src phosphorylates Tyr284 in TGF-beta type II receptor and regulates TGF-beta stimulation of p38 MAPK during breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion.Cancer Res. 2007 Apr 15;67(8):3752-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3851. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17440088
-
Grb2 binding to Tyr284 in TbetaR-II is essential for mammary tumor growth and metastasis stimulated by TGF-beta.Carcinogenesis. 2008 Feb;29(2):244-51. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgm245. Epub 2008 Jan 3. Carcinogenesis. 2008. PMID: 18174260 Free PMC article.
-
The pathophysiology of epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by transforming growth factor-beta in normal and malignant mammary epithelial cells.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2010 Jun;15(2):169-90. doi: 10.1007/s10911-010-9181-1. Epub 2010 May 15. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2010. PMID: 20467795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGF-beta control of cell proliferation.J Cell Biochem. 2005 Oct 15;96(3):447-62. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20558. J Cell Biochem. 2005. PMID: 16088940 Review.
Cited by
-
Chamaejasmenin B, a novel candidate, inhibits breast tumor metastasis by rebalancing TGF-beta paradox.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):48180-48192. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10193. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27374079 Free PMC article.
-
MYC Is a Crucial Mediator of TGFβ-Induced Invasion in Basal Breast Cancer.Cancer Res. 2016 Jun 15;76(12):3520-30. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-3465. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27197167 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of the focal adhesion complex prevents oncogenic TGF-beta signaling and metastasis.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(5):R68. doi: 10.1186/bcr2360. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19740433 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of epithelial cadherin is required to initiate metastatic outgrowth of breast cancer.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Jul 15;22(14):2423-35. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-04-0306. Epub 2011 May 25. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21613543 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular matrix as a contextual determinant of transforming growth factor-β signaling in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and in cancer.Cell Adh Migr. 2014;8(6):588-94. doi: 10.4161/19336918.2014.972788. Cell Adh Migr. 2014. PMID: 25482625 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bakin AV, Rinehart C, Tomlinson AK, Arteaga CL. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for TGFβ-mediated fibroblastic transdifferentiation and cell migration. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:3193–3206. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

