Effect of the molecular adsorbent recirculating system and Prometheus devices on systemic haemodynamics and vasoactive agents in patients with acute-on-chronic alcoholic liver failure
- PMID: 16859530
- PMCID: PMC1751025
- DOI: 10.1186/cc4985
Effect of the molecular adsorbent recirculating system and Prometheus devices on systemic haemodynamics and vasoactive agents in patients with acute-on-chronic alcoholic liver failure
Abstract
Introduction: Patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure show an aggravated hyperdynamic circulation. We evaluated, in a controlled manner, potential changes in systemic haemodynamics induced by the molecular adsorbent recirculating system (MARS) and the Prometheus system liver detoxification devices in a group of patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure.
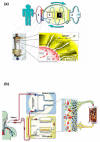
Methods: Eighteen patients (51.2 +/- 2.3 years old; Child-Pugh score, 12.5 +/- 0.2; Maddrey score, 63.1 +/- 5.0; hepatic venous pressure gradient, 17.6 +/- 0.9 mmHg) with biopsy-proven alcoholic cirrhosis and superimposed alcoholic hepatitis were either treated with standard medical therapy (SMT) combined with MARS (n = 6) or Prometheus (n = 6) or were treated with SMT alone (n = 6) on three consecutive days (6 hours/session). Liver tests, systemic haemodynamics and vasoactive substances were determined before and after each session.
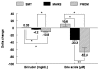
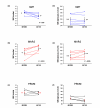
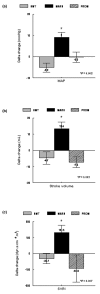
Results: Groups were comparable for baseline haemodynamics and levels of vasoactive substances. Both MARS and Prometheus decreased serum bilirubin levels (P < 0.005 versus SMT), the Prometheus device being more effective than MARS (P = 0.002). Only MARS showed significant improvement in the mean arterial pressure (Deltachange, +9 +/- 2.4 mmHg versus -0.3 +/- 2.4 mmHg with Prometheus and -5.2 +/- 2.1 mmHg with SMT, P < 0.05) and in the systemic vascular resistance index (Deltachange, +131.5 +/- 46.2 dyne x s/cm5/m2 versus -92.8 +/- 85.2 dyne x s/cm5/m2 with Prometheus and -30.7 +/- 32.5 dyne x s/cm5/m2 with SMT; P < 0.05), while the cardiac index and central filling remained constant. This circulatory improvement in the MARS group was paralleled by a decrease in plasma renin activity (P < 0.05), aldosterone (P < 0.03), norepinephrine (P < 0.05), vasopressin (P = 0.005) and nitrate/nitrite levels (P < 0.02).
Conclusion: The MARS device, and not the Prometheus device, significantly attenuates the hyperdynamic circulation in acute-on-chronic liver failure, presumably by a difference in removal rate of certain vasoactive substances. These findings suggest conspicuous conceptual differences among the albumin dialysis devices.
Figures

References
-
- Groszmann RJ. Vasodilatation and hyperdynamic circulatory state in chronic liver diseases. In: Bosch J, Groszmann RJ, editor. Portal Hypertension: Pathophysiology and Treatment. Oxford: Blackwell Science; 1994. pp. 17–26.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

