Staphylococcal enterotoxin-like toxins U2 and V, two new staphylococcal superantigens arising from recombination within the enterotoxin gene cluster
- PMID: 16861660
- PMCID: PMC1539601
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00132-06
Staphylococcal enterotoxin-like toxins U2 and V, two new staphylococcal superantigens arising from recombination within the enterotoxin gene cluster
Erratum in
- Infect Immun. 2007 Apr;75(4):2088
Abstract
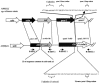
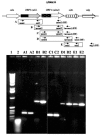
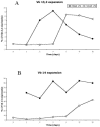
To test the hypothesis that the Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin gene cluster (egc) can generate new enterotoxin genes by recombination, we analyzed the egc locus in a broad panel of 666 clinical isolates of S. aureus. egc was present in 63% of isolates, confirming its high prevalence. The archetypal organization of the egc locus, consisting of five enterotoxin genes plus two pseudogenes, was found in 409 of 421 egc-positive strains. The egc locus was incomplete in a few strains and occasionally harbored an insertion sequence and transposase genes. These strains may represent evolutionary intermediates of the egc locus. One strain with an atypical egc locus produced two new enterotoxins, designated SElV and SElU2, generated by (i) recombination between selm and sei, producing selv, and (ii) a limited deletion in the varphient1-varphient2 pseudogenes, producing selu2. Recombinant SElV and SElU2 had superantigen activity, as they specifically activated the T-cell families Vbeta 6, Vbeta 18, and Vbeta 21 (SElV) and Vbeta 13.2 and Vbeta 14 (SElU2). Immunoscope analysis showed a Gaussian CDR3 size distribution of T-cell receptor Vbeta chain junctional transcripts of expanded Vbeta subsets in toxin-stimulated cultures, reflecting a high level of polyclonality. These data show that egc is indeed capable of generating new superantigen genes through recombination.
Figures

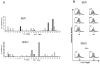

References
-
- Baba, T., F. Takeuchi, M. Kuroda, H. Yuzawa, K. Aoki, A. Oguchi, Y. Nagai, N. Iwama, K. Asano, T. Naimi, H. Kuroda, L. Cui, K. Yamamoto, and K. Hiramatsu. 2002. Genome and virulence determinants of high virulence community-acquired MRSA. Lancet 359:1819-1827. - PubMed
-
- Blaiotta, G., D. Ercolini, C. Pennacchia, V. Fusco, A. Casaburi, O. Pepe, and F. Villani. 2004. PCR detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin genes in Staphylococcus spp. strains isolated from meat and dairy products. Evidence for new variants of seG and seI in S. aureus AB-8802. J. Appl. Microbiol. 97:719-730. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

