Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is a critical downstream target of p53 in the induction of replicative senescence
- PMID: 16862142
- PMCID: PMC2954492
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb1448
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is a critical downstream target of p53 in the induction of replicative senescence
Abstract
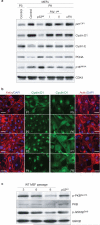
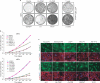
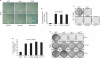
p53 limits the proliferation of primary diploid fibroblasts by inducing a state of growth arrest named replicative senescence - a process which protects against oncogenic transformation and requires integrity of the p53 tumour suppressor pathway. However, little is known about the downstream target genes of p53 in this growth-limiting response. Here, we report that suppression of the p53 target gene encoding plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) by RNA interference (RNAi) leads to escape from replicative senescence both in primary mouse embryo fibroblasts and primary human BJ fibroblasts. PAI-1 knockdown results in sustained activation of the PI(3)K-PKB-GSK3beta pathway and nuclear retention of cyclin D1, consistent with a role for PAI-1 in regulating growth factor signalling. In agreement with this, we find that the PI(3)K-PKB-GSK3beta-cyclin D1 pathway is also causally involved in cellular senescence. Conversely, ectopic expression of PAI-1 in proliferating p53-deficient murine or human fibroblasts induces a phenotype displaying all the hallmarks of replicative senescence. Our data indicate that PAI-1 is not merely a marker of senescence, but is both necessary and sufficient for the induction of replicative senescence downstream of p53.
Figures


References
-
- Lundberg AS, Hahn WC, Gupta P, Weinberg RA. Genes involved in senescence and immortalization. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2000;12:705–709. - PubMed
-
- Sherr CJ, McCormick F. The RB and p53 pathways in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:103–112. - PubMed
-
- Massague J. G1 cell-cycle control and cancer. Nature. 2004;432:298–306. - PubMed
-
- Pantoja C, Serrano M. Murine fibroblasts lacking p21 undergo senescence and are resistant to transformation by oncogenic Ras. Oncogene. 1999;18:4974–4982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

